Sic Semper Tyrannis (Latin) ("Thus Always to Tyrants") | |||||||
| Capital | Richmond | ||||||
| Largest city | Louisville | ||||||
| Other cities | Cincinnati, Virginia Beach | ||||||
| Language official |
English | ||||||
| others | French, Spanish | ||||||
| Religion main |
Protestantism | ||||||
| others | Catholicism | ||||||
| Demonym | Virginian | ||||||
| Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic | ||||||
| Legislature | General Assembly | ||||||
| President | Jim Gilmore | ||||||
| Area | 425,471 | ||||||
| Population | 22,587,688 | ||||||
| Independence | from Great Britain | ||||||
| declared | July 4, 1776 | ||||||
| recognized | 1788 | ||||||
| Currency | Dollar (VAD)
| ||||||
| Internet TLD | .va | ||||||
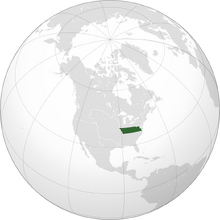
The Commonwealth of Virginia, colloquially known as Virginia, is a sovereign state located in eastern North America. The nation borders Canada and Pennsylvania to the north, Maryland to the northeast, Carolina to the south, and Louisiana to the west. The nation is bisected by the Appalachian Mountains, with the east dominated by the Atlantic Ocean and the west by the Ohio River.
Virginia was the home of the first permanent English settlement in the New World at Jamestown. Prior to which, the region of eastern Virginia was dominated by the Powhatan Confederacy. Among the reasons for the establishment of the colony was to excavate gold and silver, which were later proven to not exist on the scale England had hoped. Despite this huddle, the colony would soon become one of the wealthiest English colonies through the production and exportation of goods only produced in the New World (the largest of which was tobacco).
Virginia would play an important role during the American Revolution and would emerge as the most powerful region of the newly formed United States of America. Noted Virginians such as George Washington and Thomas Jefferson would become vital for the independence and democratization of the American Republics. Following Virginia's independence, the nation would develop into an agrarian nation and would soon compete in the production and exportation of cotton, with slave labor playing a vital role. Following the Northwest War, Virginia would secure control over the Ohio River region and settlers would begin to develop the region. The Appalachian regions would also be settled in sparser numbers and would help develop a distinct group of Virginians known as Hillbillies.
Virginia was the last American Republic to fully democratize their voting system by eliminating land ownership as a requirement to vote. During this time, Virginia's regional dominance would wane and a growing divide between Abolitionists and the pro-slavery Virginians would make the situation worse. Following the election of Abraham Lincoln in 1860, tensions between these two factions would spark a civil war in Virginia between the Commonwealth and pro-slavery rebels. General Robert E. Lee would emerge as a national figure for his role in defeating the rebel forces. Following the assassination of Lincoln in 1863, Lee would be elected president in 1864. Lee would help heal the scars between these two factions and would gradually end slavery within Virginia.
During the latter half of the 19th century, Virginia would develop closer relations with the northern American Republics, who would greatly help in the modernization of the nation. These relations would become stronger under the presidency of Woodrow Wilson.
Government and Politics[]
Political Parties[]
- Republican Party — liberalism
- Whig Party — conservatism
Subdivisions[]
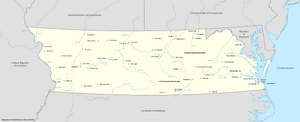
Map of Virginia.
The Commonwealth of Virginia is a unitary state comprised of around 375 counties.
| |||||