| United States of America; Etats-Unis d'Amérique | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: For the People; By our God. : Pour les Gens; Par notre Dieu. | ||||||
| Anthem: My Country 'Tis of Thee. : Mon Pays C'est de Te |
||||||
| Capital | Columbia, D.C. | |||||
| Largest city | New York City | |||||
| {{{languages_type}}} | English; French (official) | |||||
| Government | Federal constitutional presidential republic | |||||
| - | President | Barack Obama; Democratic | ||||
| - | Vice President | Joseph Biden | ||||
| - | Speaker for the Third Estate | Nancy Pelosi; Democratic | ||||
| - | Speaker for the Second Estate | Dianne Feinstein; Democratic | ||||
| - | Speaker for the First Estate | Peg Chamberlain | ||||
| Legislature | Estates-General of The United States | |||||
| American Revolutionary War from the Kingdom of France and Navarre | ||||||
| - | Constitutional Convention | May 5, 1789 | ||||
| - | Recognized | July 4, 1793 | ||||
| - | United States Constitution | May 5, 1793 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2000 census | 259,897,266 | ||||
| Currency | United States dollar ($) | |||||
The United States of America is one of the worlds largest and most influential nations. With a population of over 250 million, it is the third most populous nation on Earth, after only the People's Republic of China and the Republic of India. The Country has the world's oldest still in use constitution and one of very few remaining tricameral legislatures.
History[]
Settlement[]
The first settlers of the would be United States arrived from England. The short lived Roanoke colony was the first European settlement in the country. Jamestown was later settled by the Virginia company of London. The Province of Virginia was built un around this first settlement. Later, Plymouth Bay and other religious colonies would be built in New England and Various other Royal and Proprietary colonies. By the time of the French and Indian war, the colonies were prosperous, but after serious defeats in the hands of the French, the Colonies took it upon themselves to surrender to protect their own people. They did this without the consent of the king because they believed themselves to be in an urgent situation deserving immediate attention that the king was no of could not give. In exchange for their painless surrender, the English Colonies were permitted to keep their colonial governments with few alterations. However, these colonial legislatures did not posses the power of the purse over their territory, which would become an issue later.
The French settlers west of the English Colonies came mostly as fur trappers or wealthy peasants seeking large plantations. These colonies had not the single trace of any legislative body, elected or appointed otherwise, until 1787, when an assembly of notables was called in Paris and five notables attended from would-be U.S. territory. The king then gave his consent to these nobles to return to New France or Louisiana and assemble "wise and honorable men of property" to govern the land by the consent of the Governor.
These notables governed in Quebec north of the Great lakes long after the revolution, but in Louisiana, the Assembly would later organize an Assembly of Commoners to be elected by the populace. This was done without the consent of the king because it was a widely held belief that the king would be forced to agree to such terms in Metropolitan France upon the coming convening of the Estates-General.
Revolution[]
Appalled by the idea that they would not be represented in even the Third Estate, outrages colonial governments agreed to a constitutional convention to meet on the same day as the Estates-General would in France, May 5, 1789. Today this is known as constitution day. The Convention declared itself to be the First Continental Congress and outlined its procedures and structure within a month and the Articles of Confederation, as they were called, were approved within three. Fourteen Colonies sent delegates to the Congress. These colonies were Georgia, South Carolina , North Carolina, Virginia, Lower Quebec, Maryland, Delaware, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, New York, Connecticut, Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire. The king did not sent troops from France because he was fighting revolutionaries in Europe, instead He relied on Canada to attack the seceding colonies. The Colonies had a far larger population, but nevertheless found the Continental Congress strained to manage a war and write a permanent constitution, so in February of 1790, the Continental Congress voted to create a Second Continental Congress and a separate constitutional convention. The measure was approved almost unanimously by the legislatures of the English colonies, and by the Rump Assembly of the Illinois Country. In October 1790, the constitutional convention had finished forging their document and submitted it to the states. the measures were careful considered by each legislature and the last colony to approve of it (North Carolina) did so on May 5, 1793.
Government[]
states[]
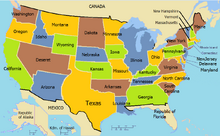
The United States of America is made up of 36 sovereign states. The states were added to the original fourteen over the course of many years. Each has equal representation in the Second Estate and Representation based on population in the third Estate. They are also permitted to appoint members of the First Estate, but the president may nominate these as well, and fully appoint them with the approval of each house of the legislature. The States are as follows:
- Maine
- New Hampshire*
- Vermont
- Massachusetts*
- Rhode Island and Providence Plantations*
- Connecticut*
- New York*
- New Jersey*
- Pennsylvania*
- Maryland*
- Delaware*
- Virginia*
- North Carolina*
- South Carolina*
- Georgia*
- Tennessee
- Kentucky
- Ohio**
- Illinois**
- Louisiana
- Arkansas
- Missouri
- Iowa
- Minnesota
- Texas
- Kansas
- Nebraska
- Dakota
- Wyoming
- Montana
- Arizona
- Deseret
- Idaho
- Washington
- Oregon
- California
*Indicates one of original seceding colonies
**Ohio and Illinois were together the Country of Illinois. They separated in 1803.
Legislature[]
Third Estate[]
The Third Estate consists of four hundred representatives of the many states elected from single seat districts for a term of two years. the Speaker for the Third Estate is elected by the members and is third in line to the presidency after the President and the Vice President.
The seats are apportioned among the states based on their populations. Each state has at least on and the states, not the Federal Government are responsible for drawing the districts.
The seats are apportioned as follows.
- Arizona - 9
- Arkansas - 9
- California - 53
- Connecticut - 5
- Dakota - 2
- Delaware - 1
- Deseret - 8
- Georgia - 21
- Idaho - 2
- Illinois - 51
- Iowa - 5
- Kansas - 5
- Kentucky - 6
- Louisiana - 4
- Maine - 2
- Maryland - 8
- Massachusetts - 10
- Minnesota - 8
- Missouri - 9
- Montana - 1
- Nebraska - 3
- New Hampshire - 2
- New Jersey - 13
- New York - 29
- North Carolina - 13
- Ohio - 18
- Oregon - 5
- Pennsylvania - 19
- Rhode island - 2
- South Carolina - 6
- Tennessee - 9
- Texas - 38
- Veromnt - 1
- Virginia - 14
- Washington - 9
- Wyoming - 1
Second Estate[]
The Second estate consists of a delegation of between three and eleven members from every state. These are assigned by the state legislatures. The current Speaker is Dianne Feinstein. The Speaker for the Second Estate is fourth in line for the Presidency after the Speaker for the Third Estate. There are currently 238 Delegates and 36 Delegations.
First Estate[]
The Delegates of the First Estate are chosen for their high moral standards and wisdom by the governors of the states. there are eight delegates from each state and 288 delegates. The First Estate holds some Judicial powers relating to the interpreting the constitution. It is generally socially conservative and less representative of the General populace than either of the other houses, but serves as an important check between the other powers.
The current speaker for the First Estate is Peg Chamberlain. The speaker is fifth in line to the Presidency after the Speaker for the Second Estate.