Europe on the map of the world
Europe comprises most of the world known to the Celts. It is the central continent in the Celtic Rules world’s economy and politics.
History of Europe[]

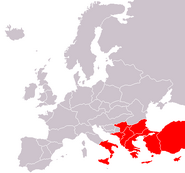
The Roman Empire at its peak
The first civilization to rise in Europe was Ancient Greece, which to a large extent set basis to later European culture.
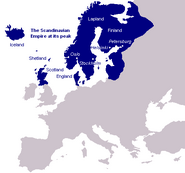
The Roman Empire once dominated the southernmost parts of Europe, and the Germanic and Slavonic tribes dwelt in northern and eastern Europe. The Germanic Viking civilization flourished in Scandinavia. Western and mainland Europe, on the other hand, being mostly inhabited by the Celtic peoples, were dominated by the Celts throughout most of the history. The Celtic Balkans once were dominated by the Slavonic-influenced Turkic tribe of Bulgarians, and the Khazars established a strong empire in the central parts of Europe, which later dissolved.
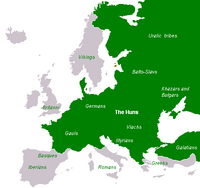
The Huns in Europe
Several peoples used to invade Europe from the neighbouring Asia, including the Slavonic-influenced Khazars and Bulgarians, and the Huns, who established a large empire in central and eastern Europe and northern Asia.
European sailors discovered lands across the Western Ocean during the period of discovery, exploration, and increase in scientific knowledge. The marine countries of western and southern Europe have established several dependencies in the Colonies region across Atlantic, and founded several colonial coastal towns in Ghana, on the coast of Black Africa.
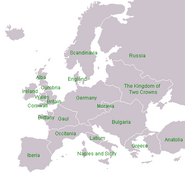
The Great European War was fought in Europe by the Axis Powers (consisting of Germany, Bulgaria, Iberia, and Occitania) and the Allied Powers (consisting of the Kingdom of Two Crowns, Russia, and various Celtic nations all across the continent). The Axis Powers were defeated and forced to give up on some parts of their territories by the Treaty of Palermo, the Kingdom of Naples and Sicily, resulting in a new political map of Europe.
Geography and extent[]

Political map of Europe
Europe spreads from the Scandinavian Peninsula on the north to the Mediterranean Sea on the south, and from the Western Ocean (Atlantic) on the west to Russia and Persia, in Asia, on the east.
There are 42 countries in Europe, some of which have long histories as independent nations while others have only appeared on the political map of Europe just recently, following the Great European War:
|
|
| The countries of Europe |
|---|
| Alba · Anatolia · Andalusia · Aragon · Arbania · Avaria · Basque · Bohemia · Bosnia · Britain · Brittany · Bulgaria · Catalonia · Cornwall · Cumbria · Dalmatia · Dioclea · England · Galicia · Gaul · Germany · Greece · Iberia · Ireland · Khazaria · Latium · Lithuania · Mœsia · Moravia · Naples and Sicily · Poland · Russia · Scandinavia · Scotland · Serbia · Sindar · Vlah · Volcæ · Wales · Wallachia · Wallonia · Welschland |
| defunct nations |
| Kingdom of Alba · Armorica · Bavaria · Cisalpine Gaul · Crimea · Epirus · Illyria · Lapland · Moldova · Two Crowns · Occitania · Rome · Sindar-Moravia · Suomi · Sweden · Syrmia |
Demographics of Europe[]
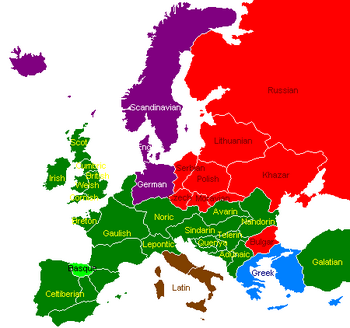
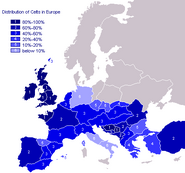
Languages of Europe
There are several ethnic groups in Europe, the largest of which are the Celtic peoples, who inhabit most of the central, western, southwestern, and southeastern parts of Europe.
The Slavonic peoples inhabit eastern Europe and parts of central Europe. They include the Russians, Serbs, Poles and other tribes. During the history they’ve influenced the Baltic Lithuanians and Turkic Khazars and Bulgarians.
Northern Europe and parts of central Europe are inhabited by the Germanic tribes such as the Germans, Anglo-Saxons, or Vikings in Scandinavia.
The south of Europe is inhabited by several Romance peoples, most notably the Romans and Napolitans.
Celtic peoples and languages[]
The Celts are the larges ethnic group in Europe.
The Celtic nations include: Alba, Anatolia, Andalusia, Aragon, Arbania, Avaria, Bosnia, Britain, Brittany, Catalonia, Cornwall, Cumbria, Dalmatia, Dioclea, Gaul, Iberia, Ireland, Mœsia, Scotland, Sindar, Stari Vlah, Volcæ, Wales, Wallachia, Wallonia, and Welschland. Significant Celtic minorities also exist in Galicia, Greece, and other countries.
Some Celtic nations – such as the countries which comprised the former Occitania – have been influenced by the neighbouring Romance peoples, and some – such as the Celtic countries of the Balkans – have mixed Celtic and Illyrian ancestry.
The Celts across Europe use different ethnonymes, including Gaul and Gæl, Welsh and Vlach, Quend (related to Celt) etc.
The Celtic languages can be divided along linguistic lines into five groups:
- Insular Celtic:
- Gælic or Goidelic group, consisting of the Irish, Scottish, and Manx languages;
- Brittonic or Brythonic group, consisting of the British, Welsh, Breton, Cornish, Cumbric, and Pictish languages;
- Continental Celtic:
- Celtiberian group, consisting of the Iberian language and its dialects in Andalusia, Aragon, Catalonia, and Iberia;
- Gaulish group, consisting of the Gaulish language and its dialects in Gaul, the Volcæ Frontier, and Wallonia, as well as the related Celtic languages and dialects spreading over the European continent, including Lepontic, Noric, and Galatian languages; and
- Vlach group in the Balkans, consisting of:
- Quendian languages, including Avarin and its dialects, Quenya with its two dialects, Telerin, Sindarin with its dialects, and Nandorin; and
- Adûnaic language and its dialects in Dalmatia, Dardania, and Dioclea.
Slavonic peoples and languages[]
The Slavs inhabit eastern Europe and some parts of central Europe. It is believed that they came to Europe from Asia. Some Slavonic peoples are extinct now, but some non-Slavonic peoples such as the Baltic and Turkic peoples in Europe and Uralic and Turkic peoples in northern Asia have been influenced by the Slavs, mostly by accepting the Slavonic language and alphabet. The Slavs themselves have been influenced by the Hunes who ruled over eastern Europe for a long time.
Slavonic nations in Europe include: Bohemia, Galicia, Moravia, Poland, Russia, and Serbia, the most prominent of which is the Russian Empire. Significant Slavonic minorities also exist in neighbouring countries, such as Lithuania, Khazaria, and Germany.
The Slavonic languages are mutually very similar and nearly almost intelligible. They are usually divided along linguistic lines into three groups:
- East Slavonic, including Russian, Lithuanian, and Khazarian;
- West Slavonic, including Polish, Serbian, Bohemian, and Moravian (which has two dialect – one in Moravia and one in Galicia); and
- South Slavonic, including Bulgarian and its dialects throughout the Balkans.
Germanic peoples and languages[]
The Germanic peoples of Europe include the Germans in Germany, the Anglo-Saxons in England, and the Vikings in Scandinavia. Significant Germanic minorities also exist in neighbouring countries, such as Serbia, Wallonia, Bohemia and others.
The Germanic dialect continuum spreads from as south as Welschland to as north as Scandinavia, and from as west as some parts of Wallonia to as east as Serbia, Poland, and Lithuania. The Germanic languages include German, English, and Scandinavian, as well as some other regional languages such as Farœse, or Bavarian in Welschland.
Romance peoples and languages[]
The Romance peoples have been influenced by the ancient Latin (Roman) culture. The Romance peoples include the Romans in Latium, and the Napolitans in the Kingdom of Naples and Sicily. Significant Romance minorities also exist in Alba Milanese, Andalusia, Aragon, Catalonia, Dalmatia, Dioclea, the Volcæ Frontier, and other countries once belonging to the Roman Empire.
The Romance peoples speak various dialects of the Latin language. Romance minorities in other countries often speak a mixture of Latin and the local non-Romance languages. These regional Romance dialects are usually referred to as the vulgar Latin or vulgar Roman.
Other peoples and languages[]
- The Slavonic-influenced Balts inhabit Lithuania. The Baltic minorities also exist in Russia and Khazaria. The original Baltic languages are extinct now, and the Lithuanian language belongs to the Slavonic language family.
- The Turkic Khazars and Bulgarians settled in the eastern parts of Europe. Their original languages are extinct now, and the Khazarian and Bulgarian languages have been influenced by the Slavonic languages to a large extent. However, they have preserved some of the original Turkic vocabulary - particularly the Bulgarian language.
- The Basques primarily dwell in the Basque Principality on the Iberian Peninsula. They speak the Basque language, which finds no relatives in other European languages.
- The Greeks traditionally inhabit Greece and neighbouring countries. They speak the Greek language.
| Languages of Europe | |||
| Celtic | Avarin · Breton · British · Celtiberian · Cornish · Cumbric · Galatian · Gaulish · Illyrian · Irish · Lepontic · Manx · Nandorin · Noric · Pictish · Quenya · Scottish · Sindarin · Telerin · Welsh | ||
| Slavonic | Bulgarian · Czech · Moravian · Polish · Russian · Serbian · Ukrainian · Weißrussian | ||
| Germanic | English (Anglo-Saxon) · German · Scandinavian | ||
| Romance | Latin · vulgar Latin | ||
| other | Basque · Greek | ||
Map gallery[]
See also[]
| Regions of the World | |||
| Europe | Balkans · Russia · Scandinavia · Iberia | ||
| Asia | Persia · India · China · Arabia | ||
| Africa | Sahara · Ghana | ||
| Colonies | Massachusetts · New Scotland · West Indies · Greenland | ||