He maketh kings to sit in soverainty;
He maketh subjects to their powre obey;
He pulleth downe, he setteth up on hy:
He gives to this, from that he takes away;
For all we have is his: what he list doe he may.
(Edmund Spenser, The Faerie Queene (1589-96), Book V, Canto II, Stanza 41)
A timeline of Cromwell the Great and events of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.
The main periods are:
- Two Lords (1658-1718, 9th to 69th Year of the Commonwealth)
- Whig Hegemony (1718-1761, 69th to 112th Year of the Commonwealth)
- British Enlightenment (1761-1790, 112th to 141th Year of the Commonwealth)
- The Age of Reforms and Revolutions (1790-1840, 141th to 191th Year of the Commonwealth)
- British Belle Époque (1840-1900, 191th to 251th Year of the Commonwealth)
Two Lords[]
(1658-1718, 9th to 69th Year of the Commonwealth)
1658[]

The funeral of Oliver Cromwell

Henry Cromwell 2nd Lord Protector of the Commonwealth (1658-1696)
- Anglo-Spanish War (1654–60).
- Northern War (1655-1660 Wars between Sweden and its adversaries).
- Publication of The Prerogative of Popular Government by James Harrington.
- 3 September - Death of Oliver Cromwell.
- 4 September - The Protector's Privy Council issues proclamation of Henry Cromwell as Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.
- 12 November - Major-General John Lambert named President of the Protector's Privy Council.
- 23 November - State Funeral of Oliver Cromwell at Westminster Abbey.
- Tea first arrived in England, exported from China via Holland.
1659[]
- Anglo-Spanish War (1654–60).
- First Esopus War (Sept 1659-July 1660 war between Dutch settlers of New Netherland against the Esopus tribe).
- Northern War (1655-1660 Wars between Sweden and its adversaries).
- Founding of the debate society The Rota Club.
- 14 January – Battle of the Lines of Elvas: The Portuguese beat the Spanish in the Portuguese Restoration War.
- 31 May – The Netherlands, France and the Commonwealth sign the Treaty of The Hague.
- Summer - Campaign and elections of the Third Protectorate Parliament. MPs to the House of Commons results in a solid majority of Cromwellian, followed by Presbyterians and an important minority faction of republican Commonwealthmen. Also elected representatives of extreme sects (such as Fifth Monarchists) and crypto-cavaliers, Catholics (from Ireland), and Episcopalians.
- July - Henry Cromwell nominates missing members needed to complete the total of 70 in the Other House.
- August - Henry Cromwell's first address to Parliament. The House of Commons by a large majority recognizes proclamation and proceeds to call for the formal installation and oath.
- November - Establishment of the Rota Club as a republican debate society founded and dominated by James Harrington.
- 7 November - Treaty of the Pyrenees between France and Spain ending the Franco-Spanish War (1635–59).
1660[]
- Anglo-Spanish War (1654–60).
- Northern War (1655-1660 Wars between Sweden and its adversaries).
- First Esopus War (Sept 1659-July 1660 war between Dutch settlers of New Netherland against Esopus tribe).
- Inauguration of Loftus College of the University of Dublin.
- Publication of The Use and Manner of the Ballot by James Harrington.
- March - Fendall's Rebellion, against Lord Baltimore. Establishment Commonwealth of Maryland.
- 23 April / 3 May – Treaty of Oliva: peace made between Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Habsburgs and Brandenburg-Prussia.
- August - Failed mutiny of army officials and troops in Jamaica.
- August - Return of Prince Rupert to England.
- 28 November - At Gresham College in London, 12 men, including Christopher Wren, Robert Boyle, John Wilkins, and Sir Robert Moray meet after a lecture by Wren and decide to found "a College for the Promoting of Physico-Mathematical Experimental Learning". Later to be known as the Society for Promoting and Improving Knowledge (SPIK).
- Hopkins Grammar School is founded in New Haven Colony.
- Navigation Act of 1660.
1661[]
- The Irish Common Prayer Book (Leabhar na hUrnaí Coitinne) is published.
- April - The Post Office introduces postmarks.
- April - Easter, and later in the same year Christmas, officially celebrated. They were suppressed between 1647-1660.
- 6 August – Portugal and the Dutch Republic sign the Treaty of The Hague, whereby New Holland (in Brazil) is formally ceded to Portugal by the Dutch Republic.
- Commonwealth Charter given out to Society of London for Promoting and Improving of Natural Knowledge (Society for Promoting and Improving Knowledge, SPIK).
- Tenures Abolition Act: Abolishes all feudal obligations to landlords, Churches and the State throughout the Commonwealth. Establishes a new taxing system for land tenure and new excise duties. It also dissolves the Court of Wards and Liveries already in recess since 1659 by Order of Council.
1662[]
- Campaign and elections of the Fourth Protectorate Parliament. Results in similar majority of Cromwellian followed by Presbyterians, a strong republican Commonwealthmen minority and others as in the previous election.
- Council of State statute the creation of two new permanent bodies: Council for Foreign Plantations and Council of Trade.
- Establishment of county commissions for keeping public peace in England and Wales
- Poor Relief Act 1662.
- The Senate Act of 1662.
- Meeting at the Savoy Palace of the main factions: Presbyterians, Independents and Episcopalians.
- Common Prayer Book and the Book of Reformed Liturgy are published.
- Koxinga's army expels Dutch from Formosa.
- 10 March - Death of Samuel Hartlib.
- April - Protector-in-Council issues commonwealth charter for Connecticut, that provides the absorption of New Haven Colony, and self government.
- 17 October - Sale of Dunkirk to France.
- Theaters allowed to stage all sorts of plays. This was banned between 1642 to 1661.
- October - Henry Cromwell's opening speech to the Parliament Principles of our Government of the Commonwealth that sketches out the Constitutional Framework of the Commonwealth.
1663[]
- First gathering of electors and nominations of the Senate, second chamber of the Parliament that replaces the Other House.
- March - Iroquois and Dutch West India Company (WIC) envoys meet at Fort Orange to sign the North River Treaty.
- 24 March - Approval of the Act of Union of Ireland, which regularizes the island's status within the Commonwealth.
- March - Amended Westminster Confession of Faith for England, Wales and Ireland. Does not included Chapters 30 and 31 on Church discipline.
- April - Act on certain measures on doctrine and organization given to the Church in Ireland to dictate. Gives to the Church of Ireland authority in a synod to establish its canons and modify the Irish Act of Faith.
- April - First issue of the Philosophical Transactions of the SPIK.
- July - September - Second Esopus War (war between Dutch settlers of New Netherland against Esopus tribe).
- September - Freeholders rebellion ousts Governor Berkeley of Virginia.
- November - Second Act of General Pardon and Oblivion.
- Enactment of the Fourth Charter of Virginia (1663).
1664[]
- Foundation of the French East India Company (Compagnie française pour le commerce des Indes orientales) to compete with the English (later British) and Dutch East India companies in the East Indies.
- Act of Settlement (of 1664 for Ireland), it also creates land registries for Ireland.
- Act for Leeward Caribbee Island Government.
- March - Act on the Organization of the Churches of England, Wales and Ireland. Creates the conjoined polity or Ussher scheme, a via media of church governance.
- April - Venner's Rising in London, Bristol and Belfast against the questionable government of Henry Cromwell. Rebels subdued and imprisoned. Hanging of Thomas Harrison, Thomas Venner, John Carew, and others. The following months purge of Fifth Monarchists from the British Army and militias. Ejectors advised to expel preachers associated with extreme sects.
- 12 June - Instrument of Government of 1664 that codifies the Principles and reforms of Henry Cromwell, outlining the basic structure, the roles, powers and responsibilities of branches of the Commonwealth government on a more permanent legal basis.
- 20 June - Licensing of the Press Act (of 1664).
- July - The Sedition Act (of 1664) and Blasphemy Act (of 1664). The last Act punishes severely independent preachers wherever they are public or unlicensed.
- August - First Joint annual session of the Trustees, Triers and Ejectors for England, Wales and Ireland.
- December - British Army and British Navy came into being with the unification of the army and navy of England, and the armies and militia of Scotland and Ireland.
- The annual Cotswold Olimpick Games were revived after being discontinued in 1642.
1665[]
- Campaign and elections of the Fifth Protectorate Parliament.
- Creation of the Commissioners for the Propagation of Christian Knowledge in Wales.
- Act for matters of government of the Church of Scotland of 1665.
- The University of Durham (founded in 1656) receives its Commonwealth Charter, giving it powers to grant its own degrees.
- The revision of The Irish Common Prayer Book (Leabhar na hUrnaí Coitinne) is published.
- Company of Adventurers Trading to Africa chartered by the Commonwealth Council of State.
- February - Outbreak of the Great London Plague.
- August - First Joint annual session of the Trustees, Triers and Ejectors for Scotland.
- September - Peak of the Great London Plague, over 7,000 deaths per week.
- November - State funerals of Elizabeth Cromwell (née Bourchier), window of Oliver and mother of Henry.
1666[]
- Establishment of shire guardians in Scotland.
- Act for the organization of the courts in Ireland.
- Act of the Government and Discipline of the National Churches of England, Wales and Ireland.
- Act of Public Monies and Endowment for Religious Observance in Scotland.
- Publication of Court Maxims by Algernon Sidney.
- Meeting the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. There were no General Assemblies between 1653 and 1665.
- February - End of the Great London Plague, city considered safe.
1667[]

The Great Fire of London
- Start of the War of Devolution (1667–68) saw Louis XIV's French armies overrun the Habsburg-controlled Spanish Netherlands and the Franche-Comté. The Triple Alliance of the Commonwealth, Sweden, and the Dutch Republic formed and secured a combined army to defend the Spanish Netherlands from the French.
- Judicature Acts of 1667.
- Parish Register Act that mandates the record of births, marriages and burials in the Civil Registers and issues marriage certificates.
- By Quinquennial Act, the House of Commons of the Parliament is to be elected every five years.
- Pope Clement IX succeeds Pope Alexander VII.
- May - first meeting of the reformed General Synod of the Church of Ireland. Its Bishop-President is appointed Archbishop of Armagh.
- 2-5 September - The Great Fire of London.
- October - First meeting of the reformed General Synod of the Church of England at London. As Bishop-President is elected the Archbishop of Canterbury, assisted by the Archbishop of York. The General Synod also approves alternately meetings of the General Synod at London and York.
1668[]
- War of Devolution (1667–68) Louis XIV is forced to give back Habsburg-controlled Spanish Netherlands and the Franche-Comté, by Spain and the Triple Alliance in the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (2 May 1668) that allowed the French to maintain their minor gains and required a monetary compensation to the Spanish in return.
- Campaign and elections of the 6th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons).
- Publication of revised Latin edition of Leviathan of Thomas Hobbes in Amsterdam to avoid the Blasphemy Act of 1664.
- Publication of An Account of the Trial of Charles I by Algernon Sidney.
- Dutch regain Island of Formosa.
- 12 August - Act organizing the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands.
- 14 August - Death of Robert Lilburne. His funeral marked the first public rally of the Levellers since 1649.
- October - Start of the legal year of the recently created High Judicial Committee.
1669[]
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- Pope Clement X succeeds Pope Clement IX.
- The Isle of Man and Channel Islands Constituencies Act. It allows for the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands to elect MPs and Senators. First elections were held in spring of 1670.
- Act of parliament that establishes land registries for England and Wales. Scotland and Ireland already had theirs respectively in 1617 and 1664.
- Reopening of City of London Exchange[1] in a new building after the old one was destroyed by the Great Fire.
- Test Acts, a series of penal laws that served as a religious test for public office and imposed various civil disabilities on Roman Catholics.
1670[]
- Establishment of county commissions for keeping public peace in Ireland.
- Public Worship Regulation Act of 1670.
- Acts strengthening the East India Company. Rights to autonomous territorial acquisitions, to mint money, to command fortresses and troops and form alliances, to make war and peace, and to exercise both civil and criminal jurisdiction over the acquired areas.
- Establishment of the second Danish East India Company.[2]
- 2 May - Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) is chartered by Parliament granting the company a monopoly over the region drained by all rivers and streams flowing into Hudson Bay (Borealia[3]) in northern Canada.
- July - Treaty of Madrid. Spain recognized English possessions in the Western Indies and Western Hemisphere. Spain also agreed to permit English ships freedom of movement in the Caribbean. Each country agreed to refrain from trading in the other's territory, and both countries agreed to limit trading to their own possessions. England agreed to suppress piracy in the Caribbean.
- Edward Somerset’s Water-commanding Engine that uses steam.
1671[]
- March - First Charter of the Danish West India Company or Danish West India–Guinea Company[4] a Dano-Norwegian chartered company for the exploitation of the colonies in the Danish West Indies.
- 12 November - Death of Sir Thomas Fairfax, Lord General of the British Army. His state funeral at Westminster Hall, the national day of mourning and the highly emotional public sorrow that was expressed by all, marked for many the end of an era of the English Revolution.
- An Act to restrain Foreign Education, prohibiting Catholics from sending their children to be educated abroad.
- First Letters patent that grants titles and honours to North Americans. It Also created the titles of landgrave and cassique [5] and new baronies for its use in the American colonies.
1672[]
- Publication of A System of Politics by James Harrington.
- April - On John Wilkins' proposal the SPIK establishes a commission for the creation of a universal standard of measure and report its implementation. Newton named Fellow of the SPIK (FSPIK).
- 7 April - Start of Franco-Dutch War 1672-1678). France declares war on the Dutch Republic. Triple Alliance renewed.
- May - Parliament dissolved (before its full term) and writ of elections issued.
- May to June - Campaign and elections of the 7th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons).
- July Lord Edward Montagu 1st Earl of Sandwich named Lord President of the Commonwealth Council of State. Former Lord President John Lambert named Commander-in-Chief of the Land Forces and President of the Army Council.
- The New Company of Adventurers Trading to Africa Act (New CATA Act) merges the old CATA with the Gambia Merchants' Company.
1673[]
- Franco-Dutch War (1672-1678).
- Catholic Exclusion Act. Expels Jesuits from the Commonwealth and confiscates their properties. Establishes severe penalties for public and private worship. Denies public rights to Catholics.
1674 (25th Year of the Commonwealth Era[6])[]
- Franco-Dutch War (1672-1678).
- First Anglican or Episcopalian Toleration Act (1676). Allows public worship, convincles and religious assemblies for Episcopalians in England.
- 14th to 20th May (Old Style)- Week of Celebration of the 25 years of the Declaration of the Commonwealth[7].
- June 1674 – April 1678 King Philip's War (war of the New England Confederation against the Native Americans).
- December - Death of Edward Hyde, 1st Earl of Clarendon.
1675[]
- Scanian War (1675-1679).
- Franco-Dutch War 1672-1678).
- Establishment of the Dominion of New England with Charles Fleetwood as its first Governor-general.
- May to June - Election and nominations of Senators.
- Promulgation of the Habeas Corpus Act (or Shaftesbury's Habeas Corpus).
- November - start construction of new St Paul's Cathedral.
- Foreign Religious Orders Act. Expels Catholic orders that do not register to local authorities, prohibits their employment as teachers and dissolves Catholic seminaries.
1676[]
- Scanian War (1675-1679).
- Pope Urban IX succeeds Clement X.
- Franco-Dutch War 1672-1678).
- Second Anglican or Episcopalian Toleration Act (1676). Allows the establishment of Episcopalian seminaries and use of property for religious services (church). The seized Catholic seminaries and properties were to be given out to the Episcopalian church and reconsecrated. Extends First Act to Scotland and Ireland.
1677[]
- Scanian War (1675-1679).
- Franco-Dutch War 1672-1678).
- May to June - Campaign and elections of the 8th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons).
1678[]
- Scanian War (1675-1679).
- Franco-Dutch War (1672-1678).
- Failed Irish-Scottish Jacobite rising of 1678.
- March - Anthony Ashley-Cooper 1st Earl of Shaftesbury named Lord President of the Commonwealth Council of State.
1679[]
- Scanian War (1675-1679).
- Treaties of Fontainebleau, Lund (both between Denmark-Norway and the Swedish Empire) and Saint-Germain-en-Laye (France and the Electorate of Brandenburg)
- 22 May - The steam digester (a high-pressure cooker with a safety valve.) built by Denis Papin is presented to members of the SPIK and general public.
- October - Death of Thomas Hobbes.
1680[]
- Publication of Discourses Concerning Government by Algernon Sidney.
- Publication of The English Liberties and the Commonwealth by James Harrington.
- Rupertine boring machine used in gun making.
1681[]

The Dutch Flower Garden built in honor of the State visit of Stadtholder Willem III
- May to June - Election and nominations of Senators.
- July - State visit of Stadtholder Willem III (widely known afterwards as the Dutch Summer).
- Posthumous publication of Behemoth: the history of the causes of the civil wars of England by Thomas Hobbes printed in Amsterdam to avoid the Blasphemy Act of 1664.
- Papin develops and builds the first safety-valve.
1682[]

Papins pressure cooker with safety valve (cooking digester Mark III 1690 Model)
- Pope Alexander VIII succeeds Urban IX.
- May to June - Campaign and elections of the 9th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons).
- Appearance of Halley's Comet.
- Papin's pressure cooker, an improved steam digester, is manufactured. The Board of Ordnance and the Commissariat put orders for pressure cookers, becoming a standard cooking equipment of the British Armed Forces.
- Episcopalian Services and Indulgence Act (Third Episcopalian Act 1676). Allows full autonomous church governance and equals rights as the rest of national churches in the Commonwealth.
- New Netherland becomes a Generality Land of the Dutch Republic, gaining full autonomy.
1683[]
- Signing of the Anglo-Dutch Concord (Engels–Nederlandse Eendracht).
- Scottish Jacobite rebellion of 1683.
- Representation and Seats of Scotland in Commonwealth Parliament (1683). The Act gives one seat to all Scottish counties, with the exception of Orkney and Shetland that share MP.
- Representation and Seats of Ireland in Commonwealth Parliament (1683). The Act gives one seat to Irish counties or neighboring groups of counties and creates an MP for the City of Dublin.
- Samuel Morland’s steam powered water-pump. He states the size of the cylinders required in his machine to raise given quantities of water per hour, and gives very exactly the relative volumes of equal weights of water and of steam under atmospheric pressure.
1685[]
- 22 October - Louis XIV revoked the Edict of Nantes, making Protestantism illegal in France. Exodus of French Huguenots most moving to the British Commonwealth and its colonies, Brandenburg-Prussia, the Dutch Republic, Switzerland, Dutch Cape Colony, New Netherland, Norway and Denmark.
1687[]
- May to June - Election and nominations of Senators and elections of the 10th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons).
- 5 July - Isaac Newton Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica or simply Principia is published.
- Joseph Dudley appointed Governor-general of the Dominion of New England.
1688[]
- Nine Years' War (1688–1697).
- Jacobite War in Ireland (1688-1690).
- Episcopalian Colonies Act (1688). Extends previous rights, privileges and toleration of Anglicans to the colonies of the Commonwealth, specifically North America. Removes various civil disabilities on Anglicans.
1689[]
- Jacobite War in Ireland (1688-1690).
- Pope Innocent XI succeeds Alexander VIII.
1690[]
- Nine Years' War (1688–1697).
- Jacobite War in Ireland (1688-1690).
- Promulgation of the Act and Declaration of Indulgence. It established complete freedom of religion and suspends or lessens punishment to Catholics in Ireland. However, the system of registration of Catholic clergy was upheld.
- Papin builds a working model of an engine, consisting of a steam-cylinder with a piston which was raised by steam-pressure, and which descended again when the condensation of the steam produced a vacuum beneath it.
1692[]
- Nine Years' War (1688–1697).
- May to June - Election of the 11th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1692-1697).
- Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold I, elevated Ernest Augustus of Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg to the rank of Elector of the Empire as a reward for aid given in the Nine Years' War.
- October - Death of Charles Fleetwood.
1693[]
- Nine Years' War (1688–1697).
- May to June - Election and nominations of Senators.
1694[]
- Nine Years' War (1688–1697).
- Scottish Jacobite rebellion of 1694.
- 27 July - Establishment of the Governor and Company of the Bank of England (Bank of England) as government lender.
1695[]
- Nine Years' War (1688–1697).
- Seven ill years (1695, 1696 and 1698–99) of famine in Scotland in the 1690s. It resulted from an economic slump created by French protectionism and changes in the Scottish cattle trade, followed by four years of failed harvests.
- Posthumous publication of Edmund Ludlow's Memoirs.
- 17 July - Establishment of The Governor and Company of the Bank of Scotland (Bank of Scotland) as government lender and commercial bank (deposit-taker and credit institution) to assist and promote Scottish business and lend to the government, subject to parliamentary approval.
1696[]

James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth 3rd Lord Protector (March 1696- July 1718)
- Seven ill years (1695, 1696 and 1698–99).
- 23 March - Death of Lord Protector Henry Cromwell (46th Year of the Commonwealth).
- April - James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth named Lord Protector.
1697[]
- Nine Years' War (1688–1697).
- May to June - Election of 12th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1697-1702).
- New issue of Letters Patent granting titles landgrave and cassique as part of installation of new Protector.
1699 (50th Year of the Commonwealth)[]
- Seven ill years (1695, 1696 and 1698–99).
- January - Louis XIV gives the Royal Academy of Sciences its first statutes. Until then it was as an informal small group of scholars that held weekly working meetings in the King's Library (1666).
- May to June - Election and nominations of Senators.
1701[]
- Great Northern War (1700–12)
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- Pope Pius VI succeeds Innocent XI.
- Coinage Union of England, Scotland and Wales making the Pound sterling the sole currency.
1702[]
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- War of the Spanish Succession (1702–1715).
- Posthumous publication of History of the Rebellion and Civil Wars in England by Edward Hyde, 1st Earl of Clarendon.
- May to June Election of 13th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1702-1703).
- Promulgation of the Claim of Rights Act. First full declaration of public and civil liberties.
1703[]
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- July-August - Election of 14th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1703-1708), previous House of Commons dissolved in April and earlier elections called by Lord Protector.
- 7 December - Great Storm of 1703. A destructive extra-tropical cyclone that struck central and southern England. The British Navy was badly affected, losing 13 ships including the entire Channel Squadron.
1704[]
- The New England Charter (1704) that dissolves all provincial legislatures.
- The Boston News-Letter starts its publication, becoming the first major newspaper of New England and British North America.
1705[]
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- New England's legislatures rebellions of 1705-1706.
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- Election and nominations of Senators.
1706[]
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- New England's legislatures rebellions of 1705-1706.
- The Standard Weights and Measures Act of 1706 that abolished obsolete, not widely used or arcane weight and measuring units and repealed local customary units used in Scotland and Ireland.
- Joint Regulations of the Mints of the Commonwealth of 1706 that created and defined the Newton degrees for metals (°N).
1708[]
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- The Haudenosaunee become a Dutch protectorate (Treaty Teantontalago / Mabee Fort).
- The Foreign Protestants Naturalization Act 1708, that allows the naturalisation of French Protestants (Huguenots), passed by Parliament only with the votes of the Whigs.
- May to June Election of 15th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1708-1712).
- George Louis officially installed the Elector-Prince of Hannover.
1709[]
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- June - Battle of Poltava. Death of King Charles XII of Sweden. His sister Ulrika Eleonora was elected Queen by the Riksdag of the Estates (July).
1710[]

Schematic of Papin's piston steam engine.
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- The Dutch Republic provides full citizens rights to Huguenot immigrants. The Spanish Netherlands already tolerated their residence.
- First diplomatic visit of Iroquois and Mahicans representatives (known incorrectly as the Four Mohawk Kings) to Dutch Republic and Britain.
- Papin's piston steam engine. A modified Somerset’s Water-commanding Engine with a safety valve and piston. Papin’s engine though more efficient than the Savery-Newcomen engine was costlier to build and accident prone due to the lack of machine boring tools to build and seal precise metal parts.
1711[]
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- Promulgation of the Act on Liberty of Religion Consciousness. It established complete freedom of religion in the Commonwealth for all Protestant and Catholics. It would by several judiciary challenges also include Judaism, Socinianism and Islam. The Act was supported by William Penn, who was widely perceived to be its instigator. It also marked the downfall of his presidency of the Council after the elections of the following year.
- Ulrika Eleanor Queen of Sweden marries Prince Charles, brother of Frederick IV King of Denmark-Norway.
1712[]
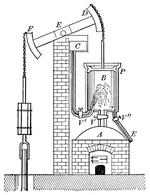
Savery-Newcomen atmospheric engine (1712). The first practical steam engine
- Great Northern War (1700–12).
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- First commercial use of the Thomas Newcomen atmospheric engine in pumping water out of a coal mine.
- Establishment of the Savery and Newcomen Engine Company as an industrial venture for manufacturing and licensing steam engines.
- July-August - Election of 16th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1712-1717), previous House of Commons dissolved in April and earlier elections called by Lord Protector.
- The Treaty of Nystad concluded between the Tsardom of Russia and the Swedish Empire ending the Great Northern War (1700–12). Russia gains Swedish Ingria, Swedish Estonia and Swedish Livonia.
1713[]
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- Peace of Utrecht. France ceded territories in dispute with Hudson's Bay Company (surroundings of Lakes Winnipegosis and Winnipeg).
- Swiss Jean Maritz invents a vertical drilling machine for cannons while in France.
1714[]
- War of the Spanish Succession.
- First Newcomen atmospheric engine installed in the Dutch Republic by Savery and Newcomen Engine Company and used to assist windmills in draining polders. Ten years later several more were built in France, Flanders, parts of Germany, Austria, Hungary and Sweden.
1715[]
- End of War of the Spanish Succession (1702–1715).
- Pope Leon XII succeeds Pius VI.
- Creation of the Grand-Duchy of Flanders.
- 1th September - Death Louis XIV of France.
1716[]
- Desaguliers introduces an improved version of the Savery-Newcomen engine, which includes safety valves and a two-way valve that operates both the steam and cold water (as opposed to two separate valves).
1717[]
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- May to June Election of 17th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1717-1722).
- Isle of Wight - Trials of Papin's steam powered paddle boat. However due to technical and design deficiencies it was not successful sinking the following year.
Whig Hegemony[]
(1718-1761, 69th to 112th Year of the Commonwealth).
1718[]

William Cavendish, 2nd Duke of Devonshire 4th Lord Protector (July 1718-June 1729)
- Ascension of the Archduchess Maria Anna Eleanor of Austria as Grand Duchess of Flanders.
- 15 July - Death of Lord Protector James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth (69th Year of the Commonwealth).
- July - William Cavendish, 2nd Duke of Devonshire named Lord Protector.
1720[]
- Jacob Leupold starts to work on the manuscript of Theatrum Machinarum Generale ("The General Theory of Machines"). Leupold includes and describes the design of a high-pressure non-condensing steam engine.
1721[]
- 26 April - Tabriz earthquake (Persian Empire). Numerous loss of lives and property.
1722[]
- Irish coinage crisis due to shortage of circulation, debased coins, inflation and rise in food prices. Previous year unusual cold weather produced crop failure in some areas.
- Riots in Belfast, Dublin and Cork. Units of the British Army called to control Ireland.
- May to June Election of 18th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1722-1727).
- Johan Willem Friso Prince of Orange-Nassau is appointed Stadtholder of the majority of provinces of the Dutch Republic
1723[]
- Pope Paul VI succeeds Leon XII.
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- 25 June - The Irish coinage crisis of 1722 leads to the establishment of the Bank of Ireland as government lender and commercial bank (deposit-taker and credit institution). Opened for business in 1725.
1724 (75th Year of the Commonwealth)[]

Inauguration of the first statue of Britannia, as an allegory of the Commonwealth. Part of the celebrations of the 75th Year of the Commonwealth (1724)
- Celebrations of the 75th Year of the Commonwealth in the British Isles and North America.
1725[]
- June - Comes into effect the incorporation of Ireland to the Coinage Union. Also the Dublin Mint reopens to provide quality coinage instead of the copper tokens.
1729[]

Charles Townshend, 2nd Viscount Townshend 5th Lord Protector (June 1729- June 1738)
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- June - Death of Lord Protector William Cavendish, 2nd Duke of Devonshire (80th Year of the Commonwealth).
- July - Charles Townshend, 2nd Viscount Townshend elected Lord Protector by Parliament on proposition of the Council of State.
1730[]
- Joseph Hornblower starts to work in an operational Leupold engine. In part an improvement of Papin’s piston steam engine.
- Death of Frederick IV, his son Christian VI became King of Denmark-Norway.
- Act for ascertaining and establishing Uniformity of Weights and Measure that standardized the customary units creating the British Exchequer Standards and redefined units, simplified the association of measurements.
- 8 July - Valparaíso earthquake severe damage and loss of lives.
1732[]
- May to June Election of 20th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1732-1737).
1734[]
- Swiss Jean Maritz further developed a method for the horizontal drilling of cannons.
1735[]
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- July - The SPIK defines the Roemer-Fahrenheit degrees (°RF) that would become the usual unit of temperature.
1736[]
- Act on the Election of Lord Protector by Parliament, passed with votes of Whig Radicals, Tories, Reformist and Country MP after proposal of the Senate is approved.
- Joseph Collingwood patents an improved Rupertine horizontal boring machine used in gun making. A shaft holds the cutting tool extended through the cylinder and is supported on both ends, unlike the cantilevered borers then in use.
1737[]
- May to June Election of 21th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1737-1743).
1738[]

John Carteret, 2nd Earl Granville 6th Lord Protector (June 1738-June 1752)
- Pope Leo XIII succeeds Paul VI.
- June - Death of Lord Protector Charles Townshend, 2nd Viscount Townshend (89th Year of the Commonwealth).
- July - First joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as electoral assembly. John Carteret, 2nd Earl Granville is elected Lord Protector.
- Charles XIII, King of Sweden on the abdication of his mother Queen Ulrika Eleanor.
1740[]
- War of the Austrian Succession (1740–48).
- Irish Famine of 1740–1741 (Irish: Bliain an Áir[8]).
- Joseph Hornblower's steam engine[9] is marketed. Establishment of Hornblower and Sons Co.
1741[]
- War of the Austrian Succession (1740–48).
- Russo-Swedish Baltic War (1741–43).
- Irish Famine of 1740–1741 (Bliain an Áir).
- Election and nominations of Senators.
1742[]
- Russo-Swedish Baltic War (1741–43).
- War of the Austrian Succession (1740–48).
- Death of Christian VI, his son Frederick V became King of Denmark-Norway.
1743[]
- War of the Austrian Succession (1740–48).
- Russo-Swedish Baltic War (1741–43).
- May to June Election of 22th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1743-1748).
- At the siege of Riga Charles XIII King of Sweden is hit and killed by an enemy bullet.
- Treaty of Åbo between Russian and Sweden ending Russo-Swedish Baltic War.
- Frederick Christian I, son of Christian VI of Denmark-Norway, is elected and crowned King of Sweden.
1744[]
- War of the Austrian Succession (1740–48).
- First Carnatic War (1744–1748). Proxy conflict between France and Britain for the control of the South of India.
- August- Louis XV king of France and Navarre dies. His son Louis XVI was enthroned as king.
1745[]
- Jacques de Vaucanson’s first completely automated loom enters production at the Royal silk plant of Lyon. Vaucanson’s automated loom is based on the work of Basile Bouchon and Jean Falcon.
1746[]
- Death of Frederick V after a long sickness leaving no immediate heir to the crown. The Riksråd elects his uncle Frederick Christian I of Sweden as King of Norway.
- 28 October - Lima–Callao earthquake. The deadliest earthquake in Peru’s history.
1747[]
- War of the Austrian Succession (1740–48).
- First Carnatic War (1744–1748). Proxy conflict between France and Britain for the control of the South of India.
- Election and nominations of Senators.
1748[]
- War of the Austrian Succession (1740–48).
- First Carnatic War (1744–1748). Proxy conflict between France and Britain for the control of the South of India.
- Pope Urban X succeeds Leo XIII.
- Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1748, by which Maria Theresa was confirmed as Archduchess of Austria and Queen of Hungary, but Prussia retained control of Silesia.
- May to June Election of 23th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1748-1753).
1749 (100th Year of the Commonwealth)[]

The British Cockade, widely worn and used in the celebrations and events of the Centenary of the Commonwealth
- Second Carnatic War (1749–1754).
- April – The first official performance of Handel's Music for the Centennial Fireworks of the Commonwealth in London. The performance marked the start of a month-long celebration.
- Willem IV is appointed Stadtholder of the majority of provinces of the Dutch Republic.
1751[]
- 25 May - Concepción earthquake (Chile).
1752[]

Archibald Campbell, 3rd Duke of Argyll 7th Lord Protector (June 1752-April 1761)
- Second Carnatic War (1749–1754).
- July - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as an electoral assembly that elects Archibald Campbell, 3rd Duke of Argyll as Lord Protector.
1753[]
- Second Carnatic War (1749–1754).
- Pope Innocent XII succeeds Urban X.
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- May to June Election of 24th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1753-1758).
1754[]
- The Commonwealth Parliament officially declares Rule, Britannia! as the national anthem of the Commonwealth.
1755[]
- 1 November - Lisbon earthquake. The combination with subsequent fires and a tsunami, the earthquake almost totally destroyed Lisbon and adjoining areas with estimates place the death toll in Lisbon alone between 10,000 and 100,000 people.
- 18 November - Cape Ann earthquake (Massachusetts Bay) Loss of property.
1756[]

The Seven Years' War.
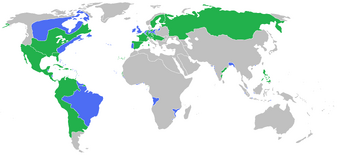
All the participants of the Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- The Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- French and Indian War (1756-1760).
- Third Carnatic War (1756–1760).
- The Conference of Boston was attended by delegates from Virginia, Maryland, New England and observers from New Netherlands to discuss better relations with the Native American tribes and common defensive measures against the French threat from Canada in the opening stage of the French and Indian War.
1757[]
- The Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- French and Indian War (1756-1760).
- Third Carnatic War (1756–1760).
- Due to the poor results of the Dominion Militia the Governor General of New England replaced it with the seven New England Militia Regiments with better payment and established its own officers' staff separate from the one of the British Army.
- Maryland and Virginia followed the example of New England and established their own permanent Provincial Regiments and officers corps, separate from the already existing Colonial Militia.
- Battle of Plassey (23 June 1757) Decisive Commonwealth victory over the Nawab of Bengal and allies. The British East India Company take control of Bengal.
- October - Death of Stadtholder Willem IV.
- December - The Dutch States General name Maurits II of Orange-Nassau General Stadholder.
1758[]
- Appearance of Halley's Comet.
- The Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- French and Indian War (1756-1760).
- Third Carnatic War (1756–1760).
- May to June Election of 25th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1758-1763).
- Indian Affairs Department established by Protector-in-Council order.
- Joint meeting of the generals of the British Army, Provincial Regiments of New England, Virginia and Maryland to coordinate actions. Attempts for equal participation of the colonies fail as the British Army assumes direct command of military campaigns.
1759[]
- The Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- French and Indian War (1756-1760).
- Third Carnatic War (1756–1760).
- Election and nominations of Senators.
1760[]
- The Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- French and Indian War (1756-1760).
- Third Carnatic War (1756–1760).
- Pope Clement XI succeeds Innocent XII.
- New England, Virginia and Maryland send colonial agents to protest creation of the Indian Affairs Department, new taxes on the colonies and demand disestablishment of Navigation Acts for North American trade.
- William Pitt's budget calls for new taxes, customs and excise duties to be applied in North America to finance loans and debts from the Seven Years' War. Approved by Parliament against opposition and lobby of the colonies.
British Enlightenment[]
(1761-1790, 112th to 141th Year of the Commonwealth).
1761[]

John Russell, 4th Duke of Bedford 8th Lord Protector (June 1761-June 1768)
- The Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- April - Death of Protector Campbell. Parliament passed the Act of Regency that establishes the Council of Regents (i.e., Commissioners of the Great Seal) to carry out part of the duties of the Protectorship until the election of June.
- June - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as electoral assembly that elects John Russell, 4th Duke of Bedford as Lord Protector.
- Clive-Dupleix Agreement that ends East Indian proxy wars between France and Britain. Originally a private communication, the revelation of its contents provokes uproars and criticism against the private diplomacy of the East India Company.
1762[]
- The Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- Ahmad Shah Durrani, Amir of Afghanistan defeats Mughal armies and kills Emperor Shah Alam II and most of the imperial family effectively ending the Mughal dynasty and installing Nadir Shah as the first Durrani emperor of Hindustan.
1763[]
- The Seven Years' War (1756-1763).
- Treaty of Paris. The British Commonwealth awarded French Canada.
- May to June Election of 26th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1763-1768).
1764[]

Union flag of the United Kingdom of Denmark-Norway and Sweden
- Union of the Crowns Denmark-Norway and Sweden with Frederick Christian I as its first King.
- Louis XVI of France assumes the title of Emperor of India[10].
- First Indian Regulating Act that established the Board of Control that supervises the East India Company.
- September - The Shakespeare Jubilee in Stratford-upon-Avon between 6 and 8 September. Marked the rising tide of bardolatry that led to Shakespeare's becoming established as the English language national poet.
- Creation of the North-West Board (NWB) for the administration, enforce law and explore the Northwest Territories.
1765[]
- Election and nominations of Senators.
1766[]
- Establishment of the British colony of Ohio out of the Northwest Territories out of the lands of the Ohio Company.
1767[]
- Parliament extends the mandate of Lord Protector to ten years.
1768[]

Granville Leveson-Gower, 1st Marquess of Stafford 9th (June 1768-June 1778) and 11th (June 1788-June 1798) Lord Protector
- Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774).
- April-May Election of 27th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1768-1773).
- June - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as an electoral assembly that elects Granville Leveson-Gower, 1st Marquess of Stafford as Lord Protector.
- Establishment of the British colonies of Illinois Country and Tennessee out of the Northwest Territories.
- Louis XVI signed the Decree of Population of the Colonies enabling unrestricted migration with official sanction and aid to Louisiana, d Guyana and later Australia.
- Battle of Janjira (8 August). Joint French-Commonwealth Fleet defeats Maratha Navy. Decisive victory enables complete British and French Control of the Kokan Coast.
1769[]
- Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774).
- Pope Alexander IX succeeds Clement XI.
- Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot builds a small version of his three-wheeled fardier à vapeur ("steam dray" or steam-tractor).
1770[]
- Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774).
- The Inclosure Act[11] created standard legal procedures that enabled enclosure of land, at the same time removing the right of commoners' access. The Act called for the appointment of Inclosure Commissioners who could enclose land without submitting a request to Parliament, thereby removing private members inclosure acts. Historically considered one of the major land reforms of the Tory-Country Coalition.
- Falklands Crisis, diplomatic standoff between Britain and Spain over possession of the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic Ocean.
- Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot's full-size version of the fardier à vapeur. Initial lack of small and effective engine curtailed further development until adoption of newer and smaller high-pressure steam engines.
1771[]
- Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774).
- Election and nominations of Senators.
1772[]
- Suleyman Shah Durrani becomes Padishah of Hindustan on the death of his father Ahmad Shah Durrani. His brother Timur Shah Durrani became the Amir of Afghanistan.
1773[]
- Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774).
- May-June Election of 28th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1773-1778).
- Louis XVI king of France and Navarre and Emperor of India dies. His son Louis XVII was enthroned as king and emperor.
1774 (125th Year of the Commonwealth)[]
1776[]
- Swearing-in and investiture of Frederik Hendrik II as General Stadholder of the Dutch Republic.
1777[]
- Election and nominations of Senators.
1778[]

Augustus FitzRoy, 3rd Duke of Grafton 10th Lord Protector (June 1778-June 1788)
- Central European War (1778-1782).
- April-May - Election of 29th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1778-1783).
- June - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as an electoral assembly that elects Augustus FitzRoy, 3rd Duke of Grafton as Lord Protector.
1779[]
- Central European War (1778-1782).
- Death of Frederick Christian I, his son Adolf Frederick was crowned King of the United Kingdom of Denmark, Sweden and Norway.
- Foundation of the French Australian colony of Cygnia, originally called Colonie du Cygnes.
1780[]
- Central European War (1778-1782).
- Fourth Silesian War (1780-1782).
- Pope Gregory XVI succeeds Alexander IX.
- Representation of the People Act (1780). Creates the political union as a unified or common electoral and political association (i.e. political party)
- Ascension of the Grand Duchess Anne-Charlotte of Flanders.
- Representation of the People Act of 1780 that expanded franchise and made wide changes in polling. Gave limited female suffrage in England, Ireland and Scotland.
1782[]
- Central European War (1778-1782).
- Fourth Silesian War (1780-1782).
- First Partition of Poland-Lithuania (1782).
- Transfer of Silesia from Austria to Prussia.
- Establishment of the British colony of New Arcadia in eastern Australia with the arrival of the First Fleet.
1783[]

The first appearance and usage of the red ballot box in the Senate elections of 1783
- May-June Election of 30th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1783-1788).
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- 8 June Eruption of Laki in Iceland. Its eight-month emission resulted in climate changes in Iceland and Europe. In Iceland the effects were disastrous.
- First Census of New England
1786[]
- The First Government Act establishes the Commonwealth of Three Nations, former Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
1787[]
- Pope Clement XII succeeds Gregory XVI.
- Establishment of the first Commonwealth and English women's college Ellisson's College for Women of London.
- Start of the long trial (1787-1795) against Warren Hastings, former Governor-general of India, for corruption and impeachment. Acquitted in 1795.
1788[]
- April-May - Election of 31th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1788-1793).
- May - Meeting of the Estates-General. A week later the Third State proclaims itself, inviting the other two states, a National Assembly. De facto end of Absolutism and establishment of Constitutional Monarchy in France.
- June - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as an electoral assembly that elects Granville Leveson-Gower, 1st Marquess of Stafford as Lord Protector.
- First National Census of the Commonwealth.
1789[]
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- July - The National Assembly becomes the National Constituent Assembly. Drafts and approves Constitution that establishes a constitutional monarchy in the Kingdom of France.
- July - The National Assembly passes the Civil Constitution of the Clergy. Creating the so-called Gallican Constitutional Church by later authors.
- The Battle of French Guiana against Dutch and British Fleets.
The Age of Reforms and Revolutions[]
(1790-1840, 141th to 191th Year of the Commonwealth).

Granville Leveson-Gower, 1st Marquess of Stafford 9th (June 1768-June 1775) and 11th (June 1788-June 1798) Lord Protector
1790[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- Elections of the French National Convention.
- 5 October 1790 - The French National Convention proclaims the Republic (14 of Vendémiaire of Year I)
1791[]

Louis XVIII King of France and Emperor of India (at Louisiana) 1791-1827
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- February - Execution of former French King Louis XVII.
- November - The National Convention approves the Constitution of Year II.
- November - At New Orleans the exiled Dauphin Louis-Auguste is proclaimed Louis XVIII King of France and Emperor of India (at Louisiana). Louisiana declares in favor of the Bourbons.
- Slave rebellion in Saint-Domingue. Beginning of the Haitian Revolution (1791-1798).
- The Republic of Mainz is proclaimed by German revolutionaries. Becoming the first German republic though short lived.
1792[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- French National Convention votes nationalization of French East India Company and allows Indian freedom of trade for French merchants.
- French East India Company breaks ties with the French Republic and allies with Royalists.
- Louis XVIII brother Prince Louis-Charles de Bourbon arrives to Pondicherry as Viceroy of India.
- Slave conspiracy in Louisiana suppressed.
- 24 October 1792[12] the French Republican Calendar was adopted and also extended it proleptically to its epoch of 22 September 1790 (Year I of the Republic). Decimal time is also established.
- The Republic of Mainz is dissolved.
- Approval for the building of Chappe's optical semaphore network (Sémaphore) after successful demonstration to government authorities for its military applications. A portable system is developed for the French Army and Navy.
1793[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- April-May Election of 32th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1793-1798).
- Scandinavian Edelcrant's system of semaphores (Optisk telegraf) is being built in the United Kingdom of Denmark, Sweden and Norway.
1794[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- 7 April (18 Germinal Year V) - The National Convention approves Décret relatif aux poids et aux mesures.[13], marks adoption of the Metric System in France.
- Rhenanian Republic (Rhenanische Republik) is proclaimed.
- British semaphore system built connecting all Channel ports with London. Murray's six-shutter system was later replaced by the more efficient Popham semaphore.
- In France the official decimal hour is defined as the mean solar time at the National Observatory - Hour of Paris (Heure de Paris).
1795[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- Corsican gained its independence from the old Genoa republic.
- Betancourt semaphore began its operation in Spain and later also used in Portugal (1801).
1796[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- New French Constitution (Constitution of Year V) establishes the Directory (five men executive).
- Slave conspiracy in Louisiana suppressed.
- Haiti (former Saint-Domingue) declares its independence from the French Republic.
- New Netherland, according to its Constitution, becomes an associated state of the Netherlands.
1797[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- Helvetic, Rhodanic and Lemanic republics established as French client states after the invasion of the old Swiss Confederation.
- 4 February - Riobamba earthquake (New Granada).
- 10 February - Sumatra earthquake.
- June - Pitt's Council of All Talents, a ruling coalition of Radical and National Reformists.
- Establishment of the Piedmontese, Etrurian and Ligurian republics in the Italian Peninsula by French troops and local revolutionaries.
- 22 September - (1st vendémiaire year VII) First edition of the Olympiads of the Republic (Olympiade de la République) in Paris, France.
- The Cult of Reason is established in France as state-sponsored deistic and civic religion by the Laws of Brumaire of year VII.
1798[]

George Spencer, 2nd Earl Spencer 12th Lord Protector (June 1798-June 1813)[14]

Adam I Kazimierz Czartoryski, King and Grand Duke of the Commonwealth of Three Nations (1798-1809)
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- April-May - Election of 33th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1798-1803).
- June - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as electoral assembly that elects George Spencer, 2nd Earl Spencer as Lord Protector.
- Adam I Kazimierz Czartoryski elected King and Grand Duke of the Commonwealth of Three Nations (1798-1809). Under the Government Act this was the last royal election beginning the reign of the House of Czartoryski.
- Establishment of the Italian Republic.
- Rauracian republic established as French client states from territories of old Swiss Confederation. Lemania votes its union to Rhodania.
- Clarmont's Rebellion and proclamation of the Quebec Republic.
- Second National Census of the Commonwealth.
1799 (150th Year of the Commonwealth)[]

Exposition des produits de l'industrie française de l'année X (1799).
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- May - Celebrations of 150th Year of the Commonwealth postponed by Parliament due to war.
- The First edition of the Exhibition of Products of French Industry of the Year X. It was the first industrial exposition in the World being the first exhibition, a showcase of French technology and industrial production. Although opened during the war it was considered an exit and further exhibitions were organized. It provided a major publicity of French achievements in the early period of the Industrial Revolution.
- British Army and Colonial regiments regain control of Quebec.
- Iskander Ghazi becomes Padishah of Hindustan on the death of his father Suleyman Shah Durrani.
1800[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- Establishment of the Roman Republic. The Pope was forced to flee. Beginning of papal interregnum.
- Establishment of the briefly lived Neapolitan Republic by French troops and local revolutionaries. Six months later it would be retaken by lazzorini and royal Neapolitan troops and the Austrian army.
1801[]

Grand Elector Emmanuel Joseph Sieyès (1801-1809).
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- Election and nominations of Senators. Pitt gains a surprising majority in the Senate
- November 1801 - Coup of Brumaire of Year XII the dismissal of the Directory and the establishment of the Grand Electorship under the (Constitution of Year XII).
- Grand Elector of the French Republic Emmanuel Joseph Sieyès ((1801-1809).
- Prince-Bishop deposed and the the Liège Republic proclaimed and declaring its neutrality.
1802[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- French and Italian republics jointly establish the Illyrian Provinces as an autonomous Italian polity.
- Rome was retaken by Austrian and Neapolitan armies. The Pope Clement XIIreturns and re-establishes the Papal States but dies a month later
- Election of Pope Pius VII.
- Peace of Amiens. Ends Revolutionary Wars. However it will last only eight months before hostilities restart with the British declaration of war.
- Republic of Mainz is re-established.
1803[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- France pressures Flanders and Belgium in signing the secret Treaty of Antwerp that gives access to Flemish and Dutch ports and gives right of passage to French troops. Treaty would become public a month later.
- April-May - Election of 34th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1803-1806). Pitt's majority was enlarged in the newly elected House of Commons.
- May - France pressures United Kingdom of Scandinavia with a naval blockade unless it is given exclusive rights of navigation for warships in the Danish Straits and consultation in case of War (The Danish Straits provocation).
- June - British declaration of war against France in answer to the Danish Straits provocation and violation of the Treaty of Amiens.
- Ragusa was annexed by the Italian Republic.
- Desaix proclaims the Republic of Egypt a French sister republic (de facto French protectorate).
- The French Army occupies and deposes the neutral government and its legislature of the republic Liège. A pro-French legislature approves the annexation of Liège to France.
1804[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- Enactment of the Government of India (Pitt's India Act).
- Death of Adolf Frederick his son Christian Gustav I crowned King of the United Kingdom of Denmark, Sweden and Norway.
1805[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- French invasion of Denmark, Sweden and Norway and the establishment of a client Scandinavia Republic.
- Prussia declares war against France and its allies.
- Battle of Iceland that concludes with the occupation of Iceland by the British Navy and Marines. Later followed by the capture of Faroe Islands and Greenland. Control of the North Sea by the British. First use of steam powered landing crafts in military action.
- A joint French-German-Scandinavian army expedition pushes into the Neva river and establishes the Novgorod Republic.
- The Free State of Hanover-Westphalia is proclaimed.
- Rheinbundakte signed between France and several western German states establishes the Confederation of the Rhine. Marshall Lazare Hoche named its Protector.
- Austrian Empire established after the Holy Roman Empire is officially declared dissolved.
- By royal proclamation Flanders is elevated from Grand Duchy to Kingdom.
1806[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- January - Death of William Pitt the Younger (1759–1806), President of the Council of State (1788-1806).
- North Sea Disaster - A third of the British Fleet lost in confrontation with the French Navy due to poor commanding and forfeit supplies.
- May - Council Crisis after the disaster of the North Sea. Fall of Council of All Talents.
- June-July - Dissolution and call for election of 35th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons) (1806-1811).
- September - Grand Court Martial for the disaster of the North Sea starts its sessions.
- Novgorod Republic reoccupied by Russia, dissolved and its leaders are either executed or exiled.
- Republic of Mainz votes its union with Rhenania.}
- Relay line London-Portsmouth built using Popham's semaphore. This system will replace Murray's system using the same previous lines.
- Pasha Muhammad Ali controls Egypt after defeating occupying French army and organizes the Khedivate of Egypt., autonomous from direct Ottoman rule.
1807[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- Election and nominations of Senators.
1808[]
- European Revolutionary Wars
- June - Reelection of Lord Protector George Spencer for a five year mandate[15].
- Restoration of the Denmark, Sweden and Norway after joint action of Coalition Forces of Britain, Prussia and Russia.
- Agreement of Stockholm between the United Kingdom of Scandinavia and Prussia creates the buffer republic of Pomerania.
- Third National Census of the Commonwealth.
1809[]

First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte (1809-1826).

Adam II Jerzy Czartoryski King and Grand Duke of the Commonwealth of Three Nations (1809-1831)
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- April 1809 - Coup of Floreal of Year XIX. Dismissal of Grand Elector Emmanuel Joseph Sieyès
- Election of First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte (1809-1826) as established under the mandate of Constitution of Year XIX.
- Crowning of Adam II Jerzy Czartoryski as King and Grand Duke of the Commonwealth of Three Nations (1809-1831)
1810[]
- European Revolutionary Wars.
- The Peace of Vienna definitely ended the Revolutionary Wars. Also, according to the Final Act of the Treaty of Vienna, the First Congress System is established.
- Rauracia and Rhodania were reincorporated into the Helvetic Republic.
- A decree of the Consulate establishes the national time for France and the Hour of Paris is renamed as the Normal Hour of France (Heure normale de France, HNF).
- Bahadur Iqbal becomes Padishah of Hindustan on the death of his father Iskander Ghazi.
- The re-established republic of Liège becomes part of Flanders by the Treaty of Vienna.
1811[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- First Dutch-Boer War.
- April-May - Election of 36th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1811-1816). The newly created National and Civic Fusion under the leadership of Spencer Perceval wins the majority.
- May - Fireworks display in London, Manchester, Bristol, Glasgow, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Dublin and Belfast to mark the postponed celebrations of 150 Year of the Commonwealth. It also started the tradition of the Hampton Court Palace Commonwealth Reception that would be regularly held each year starting 1813.
- 16 December - First Mid-Mississippi earthquake[16] (Louisiana).
- The Flemish Constitution of 1811 was promulgated.
- Concordat between France and the Pope ends schism of 1789 and reestablished the Catholic Church in France abrogating the Civil Constitution of the Clergy.
- First international convention of chapters and organizations of the Cult of Reason in Paris.
- Swearing-in and investiture of Lodewijk I as General Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic.
1812[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- First Dutch-Boer War
- Russo-Polish Peace Treaty
- The League of Thuringian States is formed.
- Haitian Army captures the Spanish colony of Santo Domingo uniting the island of Hispaniola.
- 23 January - Second Mid-Mississippi earthquake[17] (Louisiana).
- 7 February - Third Mid-Mississippi earthquake[18] (Louisiana).
- 21 December - Santa Barbara earthquake in California.
1813[]

Delmar FitzPatrick, 4th Earl of Kingston 13th Lord Protector (June 1813-June 1823).
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- First Dutch-Boer War.
- Election and nominations of Senators.
- June - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as an electoral assembly that elects Delmar FitzPatrick, 4th Earl of Kingston as Lord Protector.
1814[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- First Dutch-Boer War.
- Swiss Civil War between federalists and unitarists.
1815[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- First Dutch-Boer War.
- Monday 20 March of 1815[19] - The Italo-Iberian Civil Calendar in official use in the Italian Republic, Liguria, Etruria and Piedmont.
- 5 to 17 of April - Eruption of Mount Tambora. The Year Without a Summer (1816).
- Flemish mediation establishes the Helvetic Confederation as successor state of the former Helvetic Republic.
1816[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- April-May - Election of 37th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1816-1821). The National and Civic Fusion keeps its majority.
- Italian president Francesco Melzi d'Eril dies. Alessandro Volta named his successor.
- The Dutch East Indies Company (VOC) is nationalized by the Dutch Republic also taking control of its territories in the East Indies, Malacca and Dutch Formosa.
1817[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- Establishment of school boards as public bodies to administer elementary and vocational schools.
- Argentina, Chile and Uruguay, former colonies of Spain, declare their independence.
- The last chartered Dutch company, Dutch West Indies Company (WIC) is nationalized by the Dutch Republic taking direct control of its territories in America (Curaçao and Dependencies, Suriname and Dutch Gold Coast).
- Kaapland, former Cape Colony, is granted by the Dutch General States the condition of an associated state of the Netherlands.
- The Evangelical State Church of Prussia (Evangelische Landeskirche Preußens) becomes the sole State Church of Prussia as a United Protestant denomination.
1818[]

General Calculating Engine Mark III, Unit 4 of the Census Bureau.
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- Municipal Corporations Act (England, Scotland and Wales), established elected municipal corporations, creates fully elected county councils and county borough councils. First election schedule with the one of the Senate. Presiding officer of county councils being the County Commissioner and Shire Guardians.
- New Granada and Venezuela, former colonies of Spain, declare their independence.
- Queen Anne-Charlotte of Flanders dies. Her son Leopold I of Flanders is crowned.
- Fourth National Census of the Commonwealth. First census that used a mechanical computer (The General Calculating Engine) to tabulate results.
1819[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- Election and nominations of Senators. Radicals and reformists obtain majority for the first time.
- June - Rann of Kutch earthquake in India.
1820[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- Establishment of the Mexican Empire with Agustin I as its emperor, ending Spanish rule.
- Carlo d'Inzaghi elected president of the Italian Republic after resignation of Volta.
- March - The Evangelical League of the Rhineland (Evangelischer Bund des Rheinlandes, EBR) is formally inaugurated as the federation of the United, Lutheran and Reform churches of the Confederation of the Rhine.
1821[]

Commemorative plaque of The Channel Handshake at Saint Helier (Jersey). Inaugurated in 1861 by Lady Protectress Charlotte Hastings-Rawle and French President Pauline de La Fayette.
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- Hindustani Ghilman Revolt of 1821-1822.
- The Captaincy General of Guatemala and its depencies declare their independence from Spain and establish the United Provinces of Central America.
- The Channel Handshake between Protector FitzPatrick and First Consul Bonaparte marks a thaw in the relations of Britain and France.
- April-May Election of 38th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1816-1823). The National and Civic Fusion loses its majority and forms a minority government.
- Amazonia and Brazil became independent states from the Portuguese Empire.
- Ayesha Begum proclaimed Regent Imperial of Hindustan after her brother Padisha Bahadur Iqbal was killed by Ghilam rebels.
- Creation of the French Australian colony of Baudin, from the northern territories of Cygnia.
- Formation of the League of Thuringian States
1822[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- Hindustani Ghilman Revolt of 1821-1822.
- Pope Benedict XIII succeeds Pius VII.
- The Society for the Advancement and Rights of Women created a pressure group for women's suffrage and equal rights. It was formed one year after the French League of Women's Rights.
- After a brief civil war between Bahia and Brazil the former became independent.
1823[]

Thomas Cochrane, 10th Earl of Dundonald 14th Lord Protector (June 1823-June 1833).
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- June - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as an electoral assembly that elects Thomas Cochrane, 10th Earl of Dundonald Lord Protector.
- August-September - Early elections of 39th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1823-1828). Previous House of Commons dissolved in July and earlier elections called by Lord Protector Cochrane in an appeal to the country for a government majority in favor of reforms. Radical Progressive PU and reform allies win a clear majority.
- Novales Revolt in the Spanish Philippines defeated.
- Swearing-in and investiture of Marianne as General Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic.
- Creation of the Viceroyalty of the Antilles by the Spanish Crown. Part of the Viceroyalty are Florida, Cuba and Puerto Rico.
1824 (175th Year of the Commonwealth)[]
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- Local Government Electoral Reform Act gives single women ratepayers the right to vote in local elections. Women who owned property can be elected in local authorities elections, School Boards, Relief Boards and can be named and become Poor Law Guardians.
- Opening of the National Gallery as a government art collection on behalf of the British public. This was part of the 175th celebration of the Commonwealth.
- Quartil Agreements that establish the Italian League.
1825[]

Eleanor MacAngus-Clacher, Lady President of Scotland.
- Latin American Wars of Independence.
- August - Proclamation of the Spanish Republic.
- Election and nominations of Senators and local authorities.
- First women were named County Commissioners (five in England and two in Ireland) and Shire Guardians (three). Also Eleanor MacAngus-Clacher[20] named Lady President of Scotland.
- Riograndese became independent from Brazil.
- Peru and Alto Peru, the last Spanish colonies, became independent.
- End of the siege of Yanaon with the death of Prince Louis-Charles de Bourbon viceroy of India. The French Republic regains control of India from the Bourbons.
1826[]
- June - Death of French First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte.
- July - French Second Consul Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord resigns. Provisional First Consul Lazare Carnot elected until new elections.
- July - Proclamation of the Portuguese Republic.
- Leopold I of Flanders dies. His daughter Louise-Marie was crowned Queen of Flanders.
- The northern territories of New Arcadia become the new British colony of Cookland with its capital at Brisbane by Act of Parliament.
1827[]

Louis XIX King of France and Emperor of India (at Louisiana) 1827-1833.
- The Sultan of Lahej and the Ottoman governor were overthrown by a military coup. The Yemen Arab Republic is proclaimed.
- Louis XVIII dies. His son Louis XIX was crowned King of France and Emperor of India (at Louisiana).
1828[]
- August-September - Elections of 40th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1828-1833). Radical reformist and allied parties retain majority.
- Palmero Conspiracy in the Spanish Philippines suffocated.
- Fifth National Census of the Commonwealth.
- Act Establishing General Legislative Councils for the Presidencies of India.
- Home Civil Service Act
1829[]
- Mexican First War of the Reforms (1829-1830).
- April - Jean Bernadotte is elected First Consul (1829-1839).
- Pope Alexander X succeeds Benedict XIII.
- Yucatan declares its independence from the Mexican Empire.
- Treaty of Union, League, and Perpetual Confederation leads to the formation of the League of American Republics as an alliance of the American republics under leadership of Simon Bolivar.
1830[]
- Mexican First War of the Reforms (1829-1830).
- California, Tejas and Rio Grande, former northern provinces declare their independence from the Mexican Empire.
- Renato Alberghini elected president of the Italian Republic.
- Establishment of United Tribes of New Zealand as a federation of Maori tribes.
- Creation of the Dominion of Indiana, from the colonies and Indian territories of Ohio, Illinois Country and Tennessee, all part of the Northwest Territories.
1831[]
- Election and nominations of Senators and local authorities. No political union gains a clear majority in the Senate.
- All women that have the same franchise qualifications as men can vote and be elected.
- Establishment of the University of London by Commonwealth Charter
1832[]
- Agustin II Emperor of Mexico on the death of his father Agustin I.
- Secession of Dakota from Royalist Louisiana.
1833[]

Sir Steffen Yates, 15th Lord Protector (June 1833-June 1843).
- June - Joint meeting of both chambers of Commonwealth Parliament as electoral assembly. After a two week long of voting it elects Sir Steffen Yates.
- August-September - Elections of 41th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1833-1838). The 53 Right Honourable Ladies, the first elected female MPs.
- 25 November - Sumatra earthquake caused a large tsunami that flooded the southwestern coast of the island.
- Louisianan Revolution that overthrew the monarchy and proclaimed a republic. Louis XIX is guillotined.
- Limited local government in the Spanish Philippines.
- Rio Grande's National Congress votes its union to Tejas.
- Diplomatic collapse and dissolution of the First Congress System.
1834[]
- Pope Leon XIV succeeds Alexander X.
- The Act on the Election of Lord Protector creates an Electoral Assembly, composed of the senators and delegated-electors, for the sole purpose of electing the Lord Protector.
- The Charter of Friendship (Charte de l'amitié), is signed between France, Rhenania, Italian Republic, Kingdom of Bavaria, Commonwealth of Three Nations, Ottoman Empire and several other nations establishing the Fraternity of Nations.
1835[]

Photograph of Halley's Comet.
- Appearance of Halley's Comet.
1836[]
- Treaty of Chartres between Louisiana and Dakota ended hostilities and created the Alliance between Equals (Alliance entre égaux).
1837[]
- Election and nominations of Senators and local authorities.
- 1 January - Galilee (also called Safed) earthquake (Ottoman Empire). Numerous loss of lives and property.
1838[]
- June - San Andreas earthquake. Major loss of lives and buildings.
- August-September - Elections of 42th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1838-1843).
- Sixth National Census of the Commonwealth.
1839[]
- April - François Arago is elected First Consul (1839-1840)
British Belle Époque[]
(1840-1900, 191th to 251th Year of the Commonwealth).
1840[]
- July - French Constitution of Year L creates the office of President of the French Republic.
- August - Achille Murat elected President of the French Republic.
- The California Gold Rush.
1841[]
- The Metropolitan London Act of 1841 established the London Metropolitan Board (LMB) to administer all the metropolitan areas outside the jurisdiction of the City of London.
- 15 of June - At Badajoz, the presidents of Portugal and Spain signed the Iberian Pact that establishes the Iberian Federation.
1842[]
- Pope Alexander XI succeeds Leon XIV.
- April - Constitution of the Iberian Federation
- General Leopoldo O'Donnell elected as first president of Iberia.
1843[]

Lord Philip Cox, 16th Lord Protector (June 1843-June 1853).
- Election and nominations of Senators and local authorities.
- June - Joint meeting of delegated-electors and Senate as electoral assembly that elects Lord Philip Cox as Lord Protector.
- August-September - Elections of 43th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1843-1848).
1846[]
- Italian Crisis of 1846. President Nizzola assassinated.
- August - Odilon Barrot elected President of the French Republic.
1847[]
- Mexican Second War of the Reforms.
1848[]
- Mexican Second War of the Reforms.
- March 1848 - German Revolutions.
- Proclamation of the Free State of Hesse-Würzburg.
- August-September - Elections of 44th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1848-1853).
- General Baldomero Espartero elected president of Iberia.
- Agustin II abdicated after the Battle of Toluca. The First Mexican Republic is proclaimed.
- Swearing-in and investiture of Willem V as General Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic.
- Seventh National Census of the Commonwealth.
1849 (200th Year of the Commonwealth)[]

Crystal Palace, main exhibition building of the British Exhibition.
- British Exhibition of 1849 for the Bicentenary of the Commonwealth.
- Election and nominations of Senators and local authorities.
- Coup of Anastasio Bustamante disbands Congress and restores the Mexican Empire.
- Empress Sabina, daughter of Agustin I, is crowned before the Imperial Congress formally re-establishing the Mexican Empire.
1852[]
- August - Claude-Frédéric Bastiat elected President of the French Republic.
1853[]

Lady Charlotte Hastings-Rawle Duchess of Kent, 17th Lord Protector (June 1853-June 1863).
- June - Joint meeting of delegated-electors and Senate as electoral assembly that elects Lady Charlotte Hastings-Rawle Duchess of Kent as Lord Protector.
- Elections of 45th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1853-1854).
1854[]
1855[]
- Election and nominations of Senators and local authorities.
1858[]
- August - Pauline de La Fayette elected President of the French Republic.
- Eight National Census of the Commonwealth.
1859[]
1860[]
- General Juan Prim y Prats elected president of Iberia.
- Second Mexican Republic proclaimed with Valentín Gómez Farías as its provisional president.
- Ignacio Comonfort elected president of Mexico.
- Formation of the People's Welfare PU, splitting from the Radical Progressives.
1861[]
- Election and nominations of Senators and local authorities.
1862[]
- Slavery abolished in all of the Iberian overseas territories.
- Rebellion in Cuba.
- Elections of 48th Protectorate Parliament (House of Commons, 1862-1867).
1868[]
- Ninth National Census of the Commonwealth.
1872[]
- General Bernardo de Sá Nogueira de Figueiredo first Portuguese elected president of Iberia.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
- ↑ Called Royal Exchange until 1650
- ↑ Danish: Ostindisk Kompagni
- ↑ OTL Rupert's Land
- ↑ Danish: Vestindisk kompagni / Det Vestindisk-Guineisk kompagni
- ↑ Landgrave/Landgravines (equivalent to Earl), and Cassique/Cassica (equivalent to Viscount).)
- ↑ Act Declaring 1674 the Year of Our Lord as the 25th Year of the Commonwealth as of public observance in all the Commonwealth and its territories (1674)
- ↑ Act Declaring and Constituting the People of England to be a Commonwealth and Free-State, 19 May 1649
- ↑ The Year of Slaughter
- ↑ ATL equivalent of James Watt’s steam engine.
- ↑ In French: Empereur des Indes, in Persian: بادشاہِ ھندوستان (Badshah-e-Hind), In Hindi: भारत के सम्राट in Farsi: امپراتور هند
- ↑ An Act for the better Cultivation, Improvement, and Regulation of the Common Arable Fields, Wastes, and Commons of Pasture in this Commonwealth
- ↑ Being according to the French Republican Calendar: 3 Brumaire Year III
- ↑ Author's Note: Yes the same date, but a year earlier then OTL.
- ↑ Reelected for a mandate of five years in 1808 by the Mandate Extension (Temporary) Act of the same year
- ↑ Mandate Extension (Temporary) Act
- ↑ 1811–12 New Madrid earthquakes
- ↑ 1811–12 New Madrid earthquakes
- ↑ 1811–12 New Madrid earthquakes
- ↑ Monday 1 Primio 1815 AV. Year also rendered as 2568 AUC (Ab urbe condita)
- ↑ Or Eilionoir MacAngus-Clacher the form she favored in Scotland.
