1939[]
August[]
- 28: Hitler suffers a panic attack and is rushed to a nearby hospital.
- 29: Hitler postpones the invasion of Poland until November 1.
September[]
- 6: Hitler's psychiatrist prescribes him anti-anxiety medicine.
- 7: Hitler's psychiatrist recommends that Hitler resume painting to relieve stress.
- 17: Russia, surprised that Hitler hasn't been seen recently or invaded Poland yet, invades eastern Poland.
October[]
- 8: The Battle of Warsaw takes place, and the city falls to the Russians. Stalin requests an audience with Hitler and receives no response.
- 19: In his first public appearance in weeks, Hitler announces the permanent cancellation of the invasion of Poland. Stalin is shocked, as he has been abandoned by his potential ally and is now facing the French and British alone.
- 21: Hitler sends Stalin a message saying he is willing to intervene if the Allied forces pose a real threat to Russia. This never occurs, however, because the allies do not honor their commitment to Poland.
- 25: The Russian occupation of Poland is completed and a puppet government is set up in Warsaw.
- 30: Hitler orders that the Wehrmacht rearmament continue as planned, but despite what he has said to Stalin, makes it clear that no military conflicts are to begin until 1942 when the Wehrmacht is fully equipped, despite the Treaty of Versailles.
November[]
- 5: Russian annexation of Poland. Stalin issues an ultimatum to the Baltics, saying that if they do not align with the Soviets by the end of the year, there may be "a tragic accident" along the borders of these countries.
- 9: Adolf Hitler arranges a secret meeting with Francisco Franco of Spain, falsely warning him of a plot to undermine Fascism in Spain, and agrees to help keep him in power in exchange for Spanish assistance in the event of a war with Britain and France.
December[]
- 1: Neville Chamberlain meets with Joseph Stalin to discuss the situation in Europe and warns that Britain is prepared to respond militarily to any threat to the Baltics in an effort to keep the Baltics as potential allies.
- 3: Stalin meets with Aimo Cajander of Finland to negotiate a treaty in the event of a Russian war with Britain. Stalin is able to convince Cajander that Britain is a threat to Finnish security, resulting in the signing of the Treaty of Helsinki two days later.
- 5: The Treaty of Helsinki is signed between Russia and Finland, stating that in the event of an attack on either country, the other must come to the defense of its counterpart. It also states that Finland must also intervene in the event that Britain comes to the aid of the Baltics if Russia invades.
- 10: Stalin finalizes his plans to invade the Baltics on January 1st of 1940.
- 31: Adolf Hitler publishes his book, Mein Traum, or My Dream, in which he informs the people of Germany of his plans to avenge them for the humiliations imposed by the Treaty of Versailles.
1940[]
January[]
- 1: At 3:40 AM, a Russian soldier is killed along the Estonian border. Stalin claims that Estonian troops were responsible, and invades later that day.
- 2: Estonia is fully occupied by the Red Army. Chamberlain is scared to act on his threats to Stalin due to the slight possibility that the Estonians were actually responsible for the Russian soldier's death.
- 4: Latvia and Lithuania sign the Baltic Alliance Pact with Russia, effectively aligning them with the Soviets. Stalin installs Communist governments in these nations against the will of the people.
- 15: Inspired by Hitler's recent book, the German people of Czechoslovakia narrowly vote to allow the western half of the nation become part of Germany. Many world leaders are suspicious of this and claim that Hitler somehow rigged this vote. Nevertheless, Hitler declares this date to be a national holiday, dubbed Tag der Einheit, or Unity Day. In honor of Unity Day, Hitler announces that a museum in Berlin will be showcasing several paintings he has been working on in his absence on the first of February. Hitler's popularity rises above 50% for the first time since he became Führer.
- 23: Hitler orders Germany's top scientists to secretly begin research into a nuclear weapon.
February[]
- 1: Hitler's art show garners an audience of over a million, and many are impressed with his art. He makes his first true public appearance in months and socializes with the citizens of Germany. Support for Hitler continues to grow. Stalin begins planning to overthrow the governments of many eastern European nations to align them with the Soviet Union to increase his current perceived dominance of Europe.
- 21: A small Fascist group in Greece stages an assault on the capitol. They are put down, but succeed in making their presence known. Hitler begins to look into how he can install a Fascist government in Greece to increase his list of allies.
March[]
- 7: The United States economy suffers another stock market crash, in which those in the country who remained well off lost their fortunes, and those who were beginning to recover from the depression lose all that they had gained. Many banks are forced to close, and the U.S. dollar loses nearly all value, causing severe inflation, which just adds to the list of economic issues in America. Roosevelt's approval ratings plummet and many Americans begin to gravitate towards Communism and Fascism, noting how well they appear to be working for Russia and Germany.
April[]
- 13: Neville Chamberlain dies of a heart attack and is replaced by Winston Churchill.
- 23: Hitler secretly assists Getúlio Vargas to assume total control of Brazil in exchange for assistance in the event of war.
May[]
- 4: Hitler helps Jorge Gonzales of Chile start a revolution by staging an attack on civilians by Chilean soldiers.
- 17: Japan is able to force China's surrender by bombing Shanghai and Beijing into dust, and annexes Manchuria.
- 24: Jorge Gonzalez overthrows the Chilean government, and, contrary to what other revolutionaries believe will happen, establishes a Fascist military dictatorship.
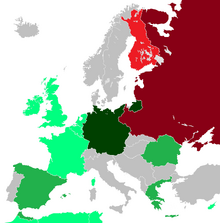
The European situation at the end of 1940. Red = ally of Russia. Green = ally of Germany Light Green = potential German ally Light Blue = colony of either France of Britain
November[]
- 5: Roosevelt's socialist platform allows him to win the presidency for the third consecutive term.
- 6: Roosevelt introduces massively socialist programs to combat the depression, which will go into effect the first of January, 1941.
- 12: Stalin agrees to fund government-sponsored programs in the United States.
- 16: Adolf Hitler orders Nazi politicians to infiltrate high into the Argentinian government and stage a full Fascist takeover
1941[]
January[]
- 1: Socialist reforms take effect in America.
- 15: Hitler's Reich puts on a spectacular light show for Unity Day. Hitler's approval rating exceeds 60% for the first time.

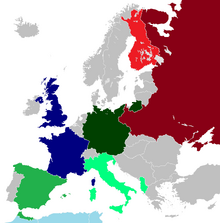
The world at the end of 1941. Dark Green = Japan or Germany Green = ally of Japan or Germany Light Green = puppet state of or occupied by Japan or Germany Blue = ally of France and Britain Light Blue = colony of France or Britain
October[]
- 9: Argentina's government is toppled and replaced by Nazi officials.
- 12: In a rigged vote, Argentina opts to begin answering to Hitler's authority. No world leaders have any evidence against Hitler, so no one decides to make a move, many believe that Fascism is soon going to become the most common method of leadership in the world.
November[]
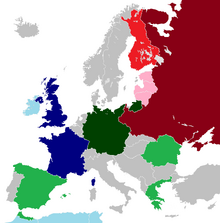
Europe at the end of 1941. Red = ally of Russia Green = ally of Germany Light Blue = colony of Britain or France Light Red = puppet state or colony of Russia
- 2: Hitler assists the Iron Guard in overthrowing the Romanian government and installs a Fascist government under Ion Antonescu.
- 30: Hitler helps Ioannas Metaxas assume total control of Greece in exchange for military support.
December[]
- 7: Japan attacks Pearl Harbor in Hawaii and destroys the majority of the American navy in the Pacific.
- 8: Japan tells Roosevelt that if he gives up Hawaii no further attacks will be carried out on the United States.
- 20: Roosevelt reluctantly gives up Hawaii to Japan after weighing the chances the U.S. has at successfully defending against Japan.
1942[]
June[]
- 27: Germany and Japan sign the Iron Sun Pact, which Italy refuses to sign.
- 30: In light of the Iron Sun Pact, Britain, Russia and America sign an agreement to share technology, and America agrees to sell weapons to Britain and Russia, but not to enter any potential war until the economy substantially improves in order to support a war.
August[]
- 1: Britain declares war on Germany and bombs the western half of the nation, losing half of the bombers they sent in. France declares war on Germany. Argentina, Brazil, Japan, Chile, Romania, Greece, and Spain declare war on France and Britain.
- 2: Hirohito meets with Hitler to discuss what should be done about colonial Europe in the Pacific. Hitler tells him to take British colonies and ignore French ones.
- 3: Japan invades British New Guinea.
- 5: British New Guinea falls to the Japanese with minimal challenge.
- 10: Japan attacks British North Borneo and Brunei.
- 16: Both British North Borneo and Brunei fall to the Japanese. Britain bombs West Germany again, this time much more effectively.
- 18: Japan invades Singapore and Malaya, facing much harsher resistance than with the previous colonial conquests.
September[]
- 1: Singapore falls into Japanese hands. Germany invades France through Alsace-Lorraine.
- 2: The Germans in Belgium invade France from the North after crushing the remaining defenses.
- 9: Malay is captured by the Japanese, eliminating all British Pacific colonies except for Australia.
- 11: Spain invades southern France and cuts off the remaining British and French from rescue.
- 12: Hirohito meets with Hitler to discuss what should be done about Australia and New Zealand, and refuses to help Germany in Europe until all threats to their Pacific dominance are dealt with. Hitler assures him that as soon as France falls, he will send the Kriegsmarine to the Pacific to help. Eldouard Daladier of France escapes to London from Paris.
- 13: The Germans reach Paris, finding it largely evacuated with only a few soldiers to defend it.
- 14: Eldouard Daladier sends Hitler France's notice of surrender. The Nazis have defeated France in just 14 days.
- 15: Winston Churchill orders the Royal Navy to form the English Channel Blockade.
- 16: Operation Sea Lion begins. 60 Nazi U-Boats assault the British blockade.
- 22: The Luftwaffe bombs Portsmouth and Hastings for the first time.
October[]
- 1: Hastings and Portsmouth are heavily bombed for the second time.
- 4: Operation Sea Lion is completed when Germany breaks through the English Channel blockade.
- 6: Congress passes Lend-Lease.
- 7: Operation Atlantis goes into effect, and Germany is able to greatly hinder America's ability to give aid to Britain. The British begin moving troops from Australia to Britain itself, in the process losing many ships and men to attacks from U-boats and Japanese bombers.
- 9: The Royal Navy and RAF begin a massive campaign to save Newport from falling to Germany.
- 13: Nearly 20% of the Royal Navy has been lost.
- 17: The Nazis are pushed back behind the blockade by heroic moves by the Royal Navy; nearly half of the Royal Navy had been destroyed. The Germans have destroyed an enormous amount of British ships in a very short time, only losing about 1000 U-boats.
- 19: Churchill delivers a speech pleading with Roosevelt to save Britain, saying that the country canot survive another attack of the caliber of Sea Lion.
- 30: Roosevelt secretly meets with Churchill, assuring him that Congress is ready to declare war as soon as the United States prepares itself to sustain a war.
November[]
- 1: Congress passes the Coastal Security Act, authorizing massive spending to secure the Pacific Coast in the event of a war with Japan.
- 2: The second phase of Operation Atlantis goes into effect and the Kriegsmarine mines the Atlantic, virtually cutting Britain off from American aid entirely.
- 7: Japan invades northern Queensland with a force of 70,000.
- 20: All of northern Australia falls to the Japanese.
- 23: Southern Australia falls.
- 26: Western Australia falls.
December[]
- 13: New South Wales falls to the Japanese.
- 14: New Zealand, and the rest of Australia surrender to the Japanese, eliminating all European presence in the Pacific.
- 21: The United States declares war on Germany and its allies.

The situation of Europe at the end of 1942
- 22: America invades Brazil with 100,000 men. The Kriegsmarine once again breaks through the British blockade and the Luftwaffe secures air supremacy over Newport by demolishing RAF bases across southern England.
- 23: Thousands of Germans storm the beaches of Brighton, Southampton and Portsmouth.
- 24: The Germans reach Bristol and the Luftwaffe begins bombing Oxford and London.
- 25: The Nazis break British defenses and storm into London as a few American ships reach British shores, only to find the nation in full retreat and chaos. Winston Churchill flees to Canada and makes it safely across the Atlantic.

The state of the world at the end of 1942
- 28: Britain surrenders, and Hitler subjects the British to the same terms Germany faced in the Treaty of Versailles with the Treaty of Geneva. The Germans take full control of the British Navy and place a Fascist dictatorship in charge of Britain and take control of its colonies, making Germany the largest empire in history.
- 29: The Americans defeat Brazil and force its citizens to be drafted into the United States military, and many of them happily agree. Later that day, the Americans take German held Guiana.
- 30: Congress passes the Unification Act, adding Canada to the United States.
1943[]
January[]
- 1: Japanese ships anchor about 70 miles from the United States, and Japanese bombers attack several large cities along the coast.
- 2: Roosevelt recovers the Japanese invasion plans from a downed plane in Portland. Later that night, German ships attack harbors on the east coast, sinking five ships in only 20 minutes, prompting Roosevelt to cancel his counter-invasion plan.
- 3: The battle continues this way for over a month.
February[]
- 5: Japanese forces break American defenses and land at beaches in California.
- 11: The Americans fight back bravely and chase the Japanese back to the ocean, where American planes begin sinking Japanese ships. The battle would remain in this state for months.
July[]
- 9: The Japanese stop fighting in the west and cancel their invasion.
- 31: Germany, Japan, and America negotiate a peace.
August[]
- 14: Germany purchase.s the Polish corridor from Stalin to ensure the security of East Prussia.
- 23: Germany invades Hungary and Slovakia, taking them the very same day.
September[]
- 1: German invades Romania.
- 18: Romania surrenders to the Germans.
- 20: Hitler meets with Refik Saydam of Turkey to plan a joint invasion of the remainder of the Balkans, in which Turkey could keep Bulgaria and Greece.
- 30: Turkey and Germany invade Bulgaria.
October[]
- 4: Bulgaria surrenders.
- 7: Turkey and Germany invade Greece, and face heavy resistance.
- 8: Turkey and Germany invade a second time, and are again expelled.
- 10: For a third time, the Turks and Germans attempt to invade and fail.
- 12: Hitler orders more equipment be sent to the invading forces, and the Germans and Turks fail to successfully invade Greece for the fourth time.
- 15: General Kleist arrives in Bulgaria, and launches a blitzkrieg against Greece, crushing its defenses and penetrating deep into Greek territory.
- 27: Turkish forces reach Athens.
- 31: Athens falls to the Turks. Later that night, Kleist launches a surprise attack on southern Yugoslavia, catching its military off guard, and moving swiftly through the nation.
November[]
- 10: Yugoslavia surrenders to the Germans.
- 13: The Second Battle of the Atlantic begins with American submarines attempting to break the Operation Atlantis lines.
- 16: Germany and Turkey annex their conquered territories.
1944[]
January[]
- 26: America breaks the southern half of the Operation Atlantis line.
- 31: Adolf Hitler hands over all middle eastern colonies to Turkey.
March[]
- 2: Nelson Mandela successfully topples the South African government and is elected Prime Minister. He then allies with the United States.
May[]
- 1: The invasion of Saudi Arabia by Germany and Turkey begins, marking the start of the First Turkish-Saudi War. The Pacific Purge begins, in which the Japanese try to rid Australia of all whites and white influence.
- 17: The Germans in west Saudi Arabia capture Medina.
- 19: The Saudis launch a successful counterattack on the Turks in the south, encircling and destroying them.
June[]
- 4: The Saudis launch a brilliant counterattack in the north using the Persian Gulf as a means of penetrating behind Turkish lines in the north, again, encircling and crushing them.
- 8: The Germans prevent a counterattack in the west.
- 10: Hitler negotiates a peace with the Saudis, in which Turkey could keep the German occupied west, but had to relinquish all territory adjacent to the Persian Gulf.
- 19: America and Saudi Arabia become allies.
- 23: The Pacific Purge has seen the deportation of 3 million Australians to Britain or America.
July[]
- 28: Hitler announces that Germany has successfully created nuclear weapons.

1944 election map. Note that California has 30 votes, Oregon 9, and Washington 10 due to the Pacific purge, and Quebec and Ontario have 3 each.
October[]
- 12: America conducts its first successful nuclear weapon test in the northern tundras of former Canada.
November[]
- 5: The Japanese crush a revolution in New South Wales, killing nearly a million in the process. All remaining whites are ordered to be executed.
- 7: William King, former Prime Minister of Canada, defeats Franklin Roosevelt for the Presidency of the United States.
1945[]
January[]
- 5: President King reverses Roosevelt's socialist policies.
- 24: Australia and New Zealand are granted freedom from Japan after their population reaches a million Japanese, and form the nation of Minami.
February[]
- 6: Operation Sisterhood begins with the American invasion of Argentina, a puppet state of Germany, as civilians cheer them on in the streets.
- 15: Argentina is secured by Americans and holds its first democratic election in years.
- 19: Chile is invaded.
- 26: Chile falls into American hands as civilians cheer.
- 27: Chile holds its first democratic elections in years.

The situation in Europe after the first part of the Hamburg agreement goes into effect
March[]
- 1: The Union of Democratic Nations (UDN) is formed by the United States, Chile, Brazil, and Argentina.
April[]
- 26: The Hamburg Agreement is reached.
October[]
- 1: Hitler signs a non-aggression pact with the Soviet Union.
- 28: Stalin signs a non-aggression pact with Japan.