| Beginning of the End |
|---|
| Timeline |
|
| Wars |
|
| Nations |
|
Timeline Part 3: in the Balance[]
Note- I am trying a different format on this page, I know that part 2 is not done, just testing it out Roguejedi 17:55, August 16, 2011 (UTC)
1949[]
The New image of Leadership[]
The revolution in Thailand, leaving a communist state, and the violence in Myanmar; along with the continued war in North Vietnam; left the people of the US feeling worried at the Asian Capitalist losses, feeling that the US was quickly losing ground against the Communists. This caused a mass dislike of the current president, Truman, and brought a previously unknown person, Micheal Roceno, into the spotlight. Roceno was smart, intelligent, and was an excellent military strategist; and so gained the hearts of the populace. Roceno promised to end Communism, and gave a few steps to make it work. He formed a new political party, with help from wealthy friends, called the Freedom Party. As the Berlin Crises and and surrender of France in Vietnam on August 9th occurred later in the year, the Freedom Party gained support steadily, while the Republican and Democrat parties lost slowly. The Korean War and the status quo resolution also angered many, thought that it let the communists off easy. The is often referred to as the "Making of the End" by many historians nowadays.
Berlin Crises heats up[]
February 31st, 1949- The USSR made a massive demand. The city of Berlin, closed off from West Germany, was to be fully integrated into East Germany, and all West Germans inside Berlin were to move to West Germany immediately.
March 2nd- The USSR threatened to declare war against the Capitalist nations if their demands were not met. US President Truman, not wanting another world war, encouraged France and Britain to pull out of Berlin.
March 5th- The order to move out was confirmed, and the East German government took control of Berlin. Many people in the US saw Truman as weak, and support for him fell.
The Formation of the Democratic Republic of Myanmar[]
Revolutions continued in Myanmar until May 15th, until the government surrendered and the revolutionaries won, creating the Democratic Republic of Myanmar, and causing massive worry In the US, seeing this as yet another loss. Myanmar elected Zuzan Chang, originally from China, and the head of the revolution, to status of president. The Democratic Republic of Myanmar quickly allied itself with Thailand, China, and the USSR, furthering the communist block. As a result, India greatly increased the number of soldiers along the border as a precaution.
Chinese Civil War cools down[]
The conquests of the People's Republic of China stopped after the takeovers of Hainan Island, the Wanshan islands and the Zhaoshan islands, with the remnant of the ROC exiled in Taiwan. The US, not wanting the fall of any more non-communist nations, sends the Seventh fleet to the Taiwan Strait as a peacekeeping force. The USSR demands that the PROC must immediately replace the ROC on the Security council to ensure "greater balance" among the council. The People's Republic of China is officially declared on October 1st, and the ROC establishes Taipei as the temporary capital.
The Seoul meetings[]
Chen Cheng from the Republic of China, Rhee Syng-man from South Korea, Yoshida Shigeru from South Japan, and Harry Truman from the United States meet in Seoul, South Korea on August 19th, 1949. They came to discuss the possibility of a four nation alliance in Pacific Asia and hoped to calm down the worries of their people. They proposed a military alliance, along with an economic alliance that would lower tariffs and increases trade between the nations. Another large riot in North Japan occurs, begging for Japanese reunification.
The Vietnam War for Independence continues[]
The Vietnam War continued throughout the year, with no resolution and the front lines just north of where they were at the end of 1948.
February 21st, 1949- the North Vietnamese forces were forced out of Da Nang, forcing them to relocate their supply lines, the first real setback of the war for Ho Chi Minn. He, making a massive tactical error, decided to continue the 5th and 7th advance into Pakxe, leaving their flank exposed.
April 4th-7th, 1949- The French struck, cutting the divisions off from their supplies and rolling them back over 75 miles. The North Vietnamese were saved from a disaster by massive unrest in South Vietnam, disrupting the French and giving the North Vietnamese valuable time.
April 22nd, 1949- Ho Chi Minh put a new general, Hoan Charoi, in charge of the 5th, 6th and 7th divisions.
June-July, 1949-Charoi immediately began to advance slowly, with a brilliant victory at Ban Taphan on June 25th and the French forces quickly fell back to defensive lines that had been built during the previous year, known as the "Ferestan Line", named after the general who envisioned it.
The advance stalled into a stalemate at Savannakhat and settled down into trench warfare for the remainder of the year. Casualties for 1949 are estimated at around 320,000 North Vietnam soldiers and 180,000 French.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization formed[]
October 1st, 1949- Postponed many times by the crises in South-East Asia and Berlin, the North Atlantic Treaty was signed by 12 North American and Western European nations in Washington D.C. The treaty was defensive in purpose, and was a deterrent to any Soviet invasion. The signing countries were: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the UK, and the US. The effectiveness of the treaty was debatable and was often thought of as weak.
The Takeover of Yugoslavia[]
June 18th, 1949- The USSR created the Yugoslavian People's Party without the knowledge of the NATO nations. The party was an exact replica of the Communist parties already prevalent in many nations
June-July, 1949- The Yugoslavian People's Party gained great numbers of followers and the USSR created the New Allies Act which offered great rewards for new communist nations. The Yugoslavian People's Party began to demand an immediate reelection. When the new election was put down, the leader of Yugoslavia mysteriously disappeared and new elections were put in place.
July 16th, 1949- The elections for the new Yugoslavian leader showed a People's Party majority (39%) and Vladimir Beshovok, descended from Russians, came into office. Yugoslavia was the newest loss for the NATO nations and the President of the US had a hard time convincing the people of the US that the capitalists still had the upper hand.
1950[]
The Korean War Begins[]
January 12th, 1950- Kim-Jung il travels to Moscow for conferences with both Stalin and Mao on plans for a communist united Korea. The NATO nations were astonished by this move and quickly formulated their own plan for a United Korea, meeting in Tokyo. Both talks are non-conclusive, but are signs of an increase in opposition.
February 2nd, 1950- A large buildup occurs in North Korea, the whole time taking care to not alert South Korea. The Korean People's Army (KPA) significantly upgraded its already formidable army. Their air force was made up of 110 Yak-9's, weak compared to US fighters but sufficient for the almost non-existent ROK army. They placed an order for another 75 T-34-85's from the USSR to complement their tank force.
February 30th, 1950- The KPA crosses the border under the guise of a South Korean pre-emptive raid. Over 500,000 soldiers are in the first wave with another 300,000 in the second. The ROK army, completely unprepared and without vehicles or an air force, is thrown into retreat. The UN Security council condemns North Korea with the USSR abstaining.
March 2nd, 1950- After a valiant defence of the city, Seoul falls to the KPA. This causes mass defections in the ROK as they continue to fall back in disarray. The United States declares war on North Korea and begins to prepare the American troops in Japan for movement into Korea. The KPA prepares for an advance on Taejon.
March 15th, 1950- The KPA advances to ten miles outside of Pusan and slows due to the presence of the United States Eighth Army. The KPA attacks the line with over 100 tanks, throwing the defenders into disarray. The People's Republic of China declares war and sends three divisions of soldiers, around 40,000 in all, into South Korea, pressuring the ROK and US to get more troops and the transfer to South Korea from Japan is increased.
March 21st, 1950- The US Eighth Army is able to decisively defeat the KPA in the Second Battle of Tinstea-Jon, breaching their line and splicing two divisions apart, creating a large breach. The newly reformed Chinese 3rd Army, consisting of eight divisions arrives, stopping the US forces. Because of this, many European nations pledge to send soldiers to Korea to oppose the Chinese.
April 3rd, 1950- The European Freedom Army, as it is dubbed, arrives in Korea. This greatly boosts the morale of ROK and US armies, who are barely holding off the Chinese storm. The EFA lands at beachheads near Inchon and are able to establish a five mile perimeter before nightfall.
April 5th, 1950- The US and European nations involved in Korea send strategists to Washington to come up with a grand battle plan and to asses the current situation.
April 20th, 1950- The EFA retakes Seoul, a great step in victory. The US Eighth Army lays siege to Taejon but the ROK, in charge of retaking the East, are thrown back at Uisong. The Chinese send 200 T-34-85's to back up their retreating forces.
May 6th, 1950- The North Koreans and Chinese are forced back continuously, only managing to hold on to the Kangwon-do and the northern Kyonggi-do provinces. US, South Korea, North Korean, and PROC diplomats meet to begin the negotiations process hoping to end the war quickly before any other countries get involved.
May 12th, 1950- An Armistice is signed in Korea, but diplomats fail to find a solution and final peace treaty. A demilitarization zone is set up and Chinese, European and US troops slowly withdraw out of Korea. This is the end of the first proxy war before the inevitable third world war.
Estimates of casualties are 20,000 EFA, 45,000 US and 150,000 ROK troops on the coalition side, and 30,000 Chinese and 200,000 KPA soldiers on the communist side. The war resolved nothing but was a testing ground for new weapons such as relying heavily on air forces for the first time.
Establishment of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam[]
January-March, 1950- The war continues as few advances are made. The French have continued hardships in Southern Vietnam as revolts and riots become commonplace. The neighboring Democratic Republic of Myanmar warns France of the dangers of continuing the war and a slow troop buildup occurs.

Southeast Asia after the fall of Vietnam
April 27th, 1950- Myanmar and Thailand declare war on French Vietnam and advance into Vietnam. This causes the distraction that the Vietnamese need and they break the French line.
May 2nd, 1950- The French forces are split into pockets and are slowly eliminated. The French sue for peace.
May 5th, 1950- The US and Europe grow angered by the fall of Vietnam but do not act due to fears relating to China and the USSR. The French officially surrender and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam is founded headed by Ho Chi Minn, and alliances are secured with all the other communist nations.
The creation of the Five Provinces[]
The USSR completed phase 1 of Plan Europe, a new Soviet plan for European conquest. The Soviet satellites in

The new division of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe were reorganized into five semi-autonomous states. This allowed greater control over the individual groups and the USSR was better able to plant people in those governments. The countries themselves were divided into "districts" dominated by various ethnic groups. this minimized the violence resulting from the change, but Austrian C.C.S. (counciliative communist state) and Yugoslav C.C.S. experienced large riots and attempts at coups. The UN and NATO quickly condemned the actions by the USSR and threatened war unless the countries were restored. The USSR adamantly declared that it would not and had support from Communist China, and the UN backed off.
United States Politics[]
The popularity of the Freedom Party continued to grow, especially in the South, more radical states. The support base was decidedly Liberal, as many of the policies included massive weapons programs and an improved defence budget. The Republican Party adopted somewhat a moderate approach to the Communist problem, not as extreme as the Freedom Party but still out there. The Democratic Party morphed to the conservative citizens who did not want a confrontation with the USSR.
Violence in Japan[]
January 26th, 1950- A dozen North Japanese militants bomb a South Japan outpost southwest of Nagano, killing five South Japanese soldiers
March 2nd, 1950- Over 100 people armed with civilian weapons mob the South Japanese embassy in the Free City of Tokyo. The police are able to arrest over 50 of the mob, without any deaths but with major damage to the area
April 13th, 1950- The terrorist group called United Japan is formed and plans to attack both North and South Japanese buildings to unite the countries.
April 24th, 1950- The first major action of United Japan is to bomb a major roadway between the cities of Chiba and Yokohama. 15 people are killed in the ensuing blast, and the road is shut down for almost a week for repairs.
May-July, 1950- United Japan and other terrorist groups remain fairly quiet, with many minor attacks. The South Japanese prime minister, Shigeru Yoshida, and Emperor Showa enacted the Safe Nation project, increasing the police budget and numbers, while modernizing them. This caused a shrinkage in the number of attacks in South Japan.
August 7th, 1950- An attempt on Shigeru Yoshida's life is discovered and foiled.
August 18th, 1950- United Japan attacks a military convoy in North Japan, destroying three light vehicles and killing 23 North Japanese soldiers, at the estimated cost of seven lives. North Japanese leader Koshida Yomata enacts a similar declaration to the Safe Nation act, but with less acting effect.
October 5th, 1950- The North Japanese embassy is bombed causing large amounts of damage and killing a dozen. The South Japanese embassy is also targeted but only causes minor damage.
November-December, 1950- Attacks again lessened but began to be focused more on the US and NATO occupation forces, trying to drive the 'foreigners" from rightful Japanese land.
1951[]
Creation of the FNPA[]
The Free Nations Pacific Alliance (FNPA) is created February 3rd, 1951 by the US, South Korea, South Japan, and Taiwan, and is an attempt to keep capitalist control of the Pacific Ocean. The alliance also declares that an attack on one country would be deemed as an attack on all and would be responded to accordingly. The USSR, North Korea, and PROC did not respond to the new alliance.
The Mexican Coup[]
March 3rd, 1951- The Mexican president, Migeul Valdes, is assassinated, causing rampant chaos and power struggles. The US demands that the assassin be found and put to justice.
March 5th, 1951- it is announced that there will be a new election in Mexico at the scheduled time, the 10th of October in 1952. The Mexican Congress elects Adolfo Cortines as the temporary president.
March 12th, 1951- The USSR approaches Adolfo knowing that he is adamantly anti-US, and offers large sums of money to stage a coup and ally with the USSR. Adolfo agrees, and begins to bring the Mexican Army to his side.
March 28th, 1951- The Mexican Congress is overthrown, and Mexico City is put under Communist control in the coup. They also gain key cities of Campeche, Merida, Leon, and Guadalajara.
April 2nd, 1951- The people's Republic of Mexico is officially announced. the US again condemns the Communists but does not do anything to stop their expansion. Adolfo Cortines becomes the head of the new Communist state.
"Fortress Cuba"[]
During the year of 1951, Fulgencio Batista overthrew Gerardo Machado and established himself as the president of Cuba. It is suspected that the USSR planned this coup at the same time as the Mexican one as Batista was another adamant anti-American. Mid-year, Batista enacted "Fortress Cuba", a plan to greatly increase Cuban military might. Construction began at the Isle of Youth as four ports were built to create a Cuban Navy. 16 forts and over 200 outposts were to line the coasts, carrying artillery and machine gun nests to stop a US attack on the island and the active military was greatly increased. It is again believed that the USSR in part paid for all of the upgrades, with help from its satellite states in Eastern Europe. The US responded by upgrading its fleet in the Gulf of Mexico and building ports on Puerto Rico.
Freedom Party spreads[]
The Freedom Party, already very known in the United States, launched offshoots in other major Capitalist nations such as France and the UK. A poll in the US stated that 23% of people would support the Freedom Party in the next election. The French Freedom Party was at 9% and the UK at 6%. Republican and Democrat Party candidates continued to adopt a more anti-USSR stance, as the public wanted a strong leader who could stop the spread of Communism. The USSR looked with concern on this new party and so sped up their conquest plans by two years.
1952[]
US election 1952[]
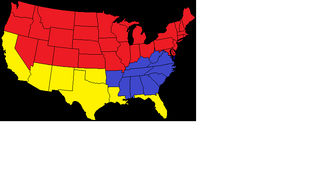
results of the 1952 elections.
The 1952 US presidential elections resulted in a major victory for Dwight Eisenhower, the Republican candidate, over Adlai Stevenson, the Democrat candidate, and Michael Roceno, the Freedom Party candidate. The election was notable for having a party other than Democrat or Republican win a large number of electoral votes. Roceno won 92 electoral votes, Stevenson won 102, and Eisenhower won 337. Roceno managed to get 28.6% of the popular vote, Stevenson won 29.1%, and Eisenhower won 42.2% of the popular vote. Eisenhower was swayed by the results to be more active in military expansion and plans to stop the USSR than would have previously occurred.
Fortress America[]
In response to the fortress Cuba program, Eisenhower almost immediately implemented the Fortress America program. It was an effort to modernize the US army. The money was drawn from the results of the shrinkage of other government programs. The program called for the complete rearming of the army. These improvements included developing a heavy tank capable of wielding a 105mm gun, an improved APC, replacing the new M75, an improved Self-propelled artillery piece, and a redone air force. This program was very advertised, intended to increase the confidence in the US
War Plan Red[]
the USSR secretly created their war plan for an invasion of Europe, jointly with the other communist states. The

the proposed division of Eurasia, with USSR and Chinese satellite states
plan emphasized large use of armoured units and heavy bombings. The plan involved the use of three prongs: a central massive strike in continental Europe, a smaller pushing through Scandinavia, and a third invading Italy and southern France. The meager Soviet Navy was to try to secure the Mediterranean by conquering Gibraltar. The Soviet Air Force would use German and Scandinavian airports to quickly try to neutralize the UK and the settle in for the American forces to arrive then use weight of numbers to crush them.
Operation "Newfound Freedom"[]
NATO, as its first major act since its conception, began Operation "Newfound Freedom" as an effort to increase support of capitalism around the world, especially in places that were unsure what side to join. They created the Activist Broadcasting Organization, a well funded media company whose sole purpose was to expose the "horrors" of communism through a series of television broadcasts. The series was released in seven half-hour episodes, but the distribution around the world was spotty and few people in rural or undeveloped areas had the technology to view these videos. While not altogether a failure, Operation "Newfound Freedom" soon became an example of the futility of peace talks among the American populace, causing further support for drastic measures.
The "Finnish Wall"[]
Late in 1952, as an effort to counteract a possible Soviet invasion, the Finnish military began the construction of a series of border defenses around the southern border between the USSR and Finland. The wall was to be constructed much like the French Maginot line, with "fortresses" every five miles, equipped with a heavy cannon and a few bunkers for machine gun emplacements. Rear artillery areas were to be set up, mostly around the vicinity of Lappeenranta near the Baltic Sea. While ideally this would be able to hold a major Soviet invasion, the practicality of it was very low. The Finnish simply did not have enough resources to build such a massive feat, so what resulted was a half-done barrier that was filled with weaknesses, not any real protection. This did, however, strengthen the morale of the Finnish people, many of whom did not know the slightest thing about military strategy, and who saw the imposing structures as invincible and unassailable.
