Nazi parade in Paris after its fall
World War II, or the Second World War, (often abbreviated WWII or WW2) was a global military conflict which involved a majority of the world's nations, including all of the great powers, organised into two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. The war involved the mobilisation of over 130 million military personnel, making it the most widespread war in history. In a state of "total war", the major participants placed their complete economic, industrial and scientific capabilities at the service of the war effort, erasing the distinction between civilian and military resources. Over 100 million people, the majority of them civilians, were killed, making it the deadliest conflict in human history.
The start of the war is generally held to be in September 1938 with the German invasion of Poland and subsequent declarations of war on Nazi Germany by the British Commonwealth and France. Many belligerents entered the war before or after this date, during a period which spanned from 1937 to 1941, as a result of other events. Amongst these main events are the Marco Polo Bridge Incident (fought between Nationalist China and Japan), the start of Operation Barbarossa (the Nazi invasion of Russia), the Operation Huanan Paca (the Incan invasion of the Aztecs), and the attacks on Pearl Harbor and British and Dutch colonies in South East Asia.
The Russian Empire, the Aztec Empire and the United States emerged from the war as the world's superpowers. This set the stage for the Cold War, which lasted for the next 22 years. The United Nations was formed in the hope of preventing another such conflict. The self-determination spawned by the war accelerated decolonisation movements in Asia and Africa, while Western Europe itself began moving toward integration.
Sides[]
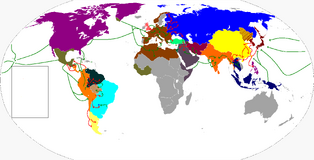
World during WWII
Allies
- Aztec Empire
- United States
- China
- Russia
- Muslim Confederation
- Republic of Great Colombia
- Bahasa Confederation
- France
- England
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Poland
- Czechoslovakia
- Norway
- Denmark
- Netherlands
- Greece
- Cuba
- Brazil
- Turkey
- Egypt
- Patagonia Republic
Axis
- Incan Empire
- Reich III
- Italy
- Japan
- Spain
- Amazonic Republic
- India
- Persia
- Hungary
- Romania
- Bulgaria
- Yugoslavia
- Manchukuo (Manchuria)
- Slovakia
War in America[]
See also: War in America
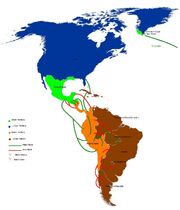
Moves in WWII on America
This front started with the invasion of the Incan Empire to the Aztec Empire in 1941. The Incan Empire tried to launch attacks in three different parts of the Anahuac:
The first invasion point was in the Yuuk'aatan peninsula, and there the Incan forces could take control from important ports like Tulum. On the first part of the invasion to the peninsula, the Incans were victorious in the Belize naval battle, taking control of Tulum, Xetumal and Kaankum. Then the Incans advanced to the center of the peninsula with the purpose of taking Chichen itza at the Chichen Itza Battle, where the Incans were defeated by the Aztec/American union.
The second was the invasion by land of the Aztec province of Huatemalli, taking control of Mixco, but this front was heavy repelled and the city recaptured in the next month.
The third point was the invasion of the Aztec Pacific coast. This one was repelled fast and effectively by Aztec Forces, especially the Aztec Navy.
The Republic of Great Colombia entered to war in 1942, when the Incans invaded the border city of Huanasintuyo and the Amazonia Republic invaded the south part of the country. The Republic rapidly repelled the Amazonic invasion and immediately tried to invade its southern neighbor; but the Inca offensive was more difficult to contain, the forces Incas even managed to take half from the country. The Inca invasion wasn't successfully repelled until 1944, when the Aztec, American and Brazilian forces could take a great part of the Incan territory, including the north part and the coast.
Eastern Front[]
See also: Operation Barbarossa

German artillery at the Sebastopol siege
The Eastern Front of World War II (German: die Ostfront 1941-1945, der Rußlandfeldzug 1941-1945 (Russian campaign) or der Ostfeldzug 1941-1945 (Eastern Campaign)) was a theatre of war between the German Reich and the Russian Empire which encompassed central and eastern Europe from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. Nazi propaganda dubbed the conflict Battle for Survival against Slavs or a Crusade against the Slavs. In the majority of Russian sources, the military conflict in Eastern Europe is referred to as the Great Patriotic War, but sometimes that phrase also includes operations against Imperial Japan in 1945. Some scholars of the conflict use the term Russo-German War, while others use the Nazi-Russian War or Axis-Russian War.
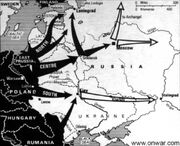
Operation Barbarossa
It was the largest theatre of war in history and was notorious for its unprecedented ferocity, destruction, and immense loss of life. It bore the bulk of the Holocaust (or Shoah), and stands unparalleled in terms of the volume of scholarly analysis and cultural depictions it generated (films, books, video games etc.). More people fought and died on the Eastern Front than in all other theatres of World War II combined. With over 30 million dead, many of them civilians, the Eastern Front has been called a war of extermination. It resulted in the destruction of the Third Reich, the partition of Germany and the rise of the Russian Empire as a military and industrial superpower.
The series of events preceding the opening of the Eastern Front included the invasion of Poland in 1939 by Nazi Germany and the resulting fourth partition of Poland when the Russian Empire used the invasion as a pretext to annex the eastern regions of the country, populated by a majority of ethnic Ukrainians and Belarussians and by Polish minorities, as outlined in the secret codicil to the August 1939 Russian-German non-aggression pact, which also paved the way for the 1940 Russian occupation of Bessarabia.
Western Front[]
- See also: Operation Sealion, Battle of Britain

D-Day disembark in Normandy
The Western Front of the European Theatre of World War II encompassed the United Kingdom, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Norway, and Denmark. The Western Front was marked by two phases of large-scale ground combat operations. The first phase saw the defeat of France and the Low Countries during May - June, 1940, followed by Germany's aerial assault on Great Britain. The second phase of large-scale ground combat commenced in June 1944 with the Allied landings in Normandy and continued until the defeat of Germany in May 1945.
War in the Pacific[]
The Pacific War was the part of World War II—and preceding conflicts—that took place in the Pacific Ocean, its islands, and in East Asia, between July 7, 1937 and August 14, 1945. The most decisive actions took place after the Empire of Japan attacked various countries which together came to be known as the Allies (or Allied powers).
The Axis states which assisted Japan included the authoritarian government of the Republic of India. The Japanese puppet states of Manchukuo (parts of Manchuria and Inner Mongolia) and the Wang Jingwei Government (which controlled the coastal regions of China). Japan enlisted many soldiers from its colonies of Korea and Formosa (later known as Taiwan). To a small extent, some Vichy French, Indian National Army, and Burmese National Army forces were active in the area. To an even smaller extent, German and Italian naval forces (mainly armed merchantmen and submarines) also operated in the Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean.
The major Allied participants were the Aztec Empire, United States (including forces of the Commonwealth of the Philippines), China, the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand, Free France and many other countries also took part, especially forces from other British colonies.
The Russian Empire fought two short, undeclared border conflicts with Japan in 1938 and 1939, then remained neutral until August 1945, when it joined the Allies and invaded the territory of Manchukuo, Republic of China, Inner Mongolia, the Japanese protectorate of Korea and Japanese-claimed islands such as Sakhalin coordinated notably between the Red Banner Pacific Fleet and the US Navy's Task Force 38.

American/Aztec atomic bomb that the allies drop over Japanese cities
Between 1942 and 1945, there were four main areas of conflict in the Pacific War: China, the Central Pacific, South East Asia and the South West Pacific.
U.S. sources refer to two theaters within the Pacific War: the Pacific Theater of Operations (PTO) and the China Burma India Theater (CBI). However these were not operational commands. In the PTO, the Allies divided operational control of their forces between two supreme commands, known as Pacific Ocean Areas and Southwest Pacific Area.
In 1945, for a brief period just before the Japanese surrender, the Russian Empire and its Mongolian ally engaged Japanese forces in Manchuria and northeast China.
Aftermath[]

The Incan city of Arequipa after an Aztec bombardment
In an effort to maintain international peace, the Allies formed the United Nations, which officially came into existence on October 24, 1945. Regardless of this though, the alliance between the Western Allies and the Russian Empire had begun to deteriorate even before the war was over, and the three powers each quickly established their own spheres of influence. In Europe, the continent was essentially divided between Western and Russian spheres by the so-called Iron Curtain which ran through and partitioned Allied occupied Germany and occupied Austria. In Asia, the United States occupied Japan and administered Japan's former islands in the Western Pacific while the Russians annexed Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands; the former Japanese governed Korea was divided and occupied between the two powers. Mounting tensions between the United States and Russia soon evolved into the formation of the American/Aztec-led NATO and the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact military alliances and the start of the Cold War between them.
Casualties and Losses[]

Combined Aztec/American Air Division in the battle of Midway
Estimates for the total casualties of the war vary, but most suggest that some 90-100 million people died in the war. Many civilians died because of disease, starvation, massacres, bombing and deliberate genocide. The Russian Empire lost around 30 million people during the war, about a third of all World War II casualties. Of the total deaths in World War II, approximately 85 percent were on the Allied side (mostly Russian and Chinese) and 15 percent on the Axis side. One estimate is that 12 million civilians died in Nazi concentration camps, 1.5 million by bombs, seven million in Europe from other causes, and 7.5 million in China from other causes. Figures on the amount of total casualties vary to a wide extent because the majority of deaths were not documented.