| This article is under construction. Please don't edit or add to this article unless you are a member of Axis vs Allies Revised (Map Game). Propose any changes to the talk page. |
"Libertad o muerte" (Spanish) "Liberty or death" (English) | |||||||
| Capital | Caracas | ||||||
| Largest city | Bogotá | ||||||
| Other cities | Ciudad Bolívar, Maracay, Maturín, Cuidad de Guyana, Managua, San Salvador, Panama City, lima, La Palz, Medellín, Sucre, Cusco, Santiago de Chile, Cali and Asuncion. | ||||||
| Language official |
Spanish | ||||||
| others | Amerindian languages and American English | ||||||
| Religion main |
Roman Catholic Christianity | ||||||
| others | Native creeds | ||||||
| Government | Military Dictatorship ( 1939 elections fixed) | ||||||
| Legislature | The national junta via a puppet parliament | ||||||
| President | Lt General Oscar Aznar | ||||||
| Population | 42,600,800 est.- (1956) | ||||||
| Established | 1829 | ||||||
| Independence | from Spain | ||||||
| Currency | Venezuelan Bolívar | ||||||
| Organizations | UN, Global Alliance for Democracy, League of Catholic Nations, NPT, Latin American Economic and Monetary Union, ESEA. | ||||||
Venezuela proper, is a tropical, oil rich, Hispanic, rain forest country on the northern coast of South America.
Geography[]
Our timeline Venezuela, Netherlands Antilles, western and central Nicaragua, Guayana, Tobago, Panama (less the Canal Zone), Chile, Colombia, El Salvador, Peru, Bolivia, Paraguay, Colombia and the Darién Gap. Venezuela proper (OTL Venezuela) has a total area of 916,445 sq km (353,841 sq mi) and a land area of 882,050 sq km (340,560 sq mi).
History[]
Pre-1947[]
An army coup took place in 1933 removing the OTL dictator and replacing him with the ATL General Aznar, who took over with the aim of becoming a local, regional and Latino strong man.
Venezuela faced a rebellion by counter revolutionary forces in many of its cities towards the middle of 1934. The army’s attention turned inwards and focused on national stability and the regime's survival. The leftist rebellion was thankfully quashed after two months. The El Distrito Metropolitano de Caracas and Ciudad Bolívar were to remain under martial law for another year due to persistent resistance by some local rebel cells. A later urban rebellion also occurred in Caracas City during 1947.
The new Junta's first foray in to Venezuela-USA affairs was with the signing of a 40 year long oil trade agreement in 1935. Venezuelan Overseas Intelligence Agency (V.O.I.A.) is formed in 1935 to do espionage and special ops work, it was one of the first organisations of this kind in the world.
Venezuela then went on to condemn nuclear and chemical warfare as early as 1937, and then joined the NPT in 1946. The anti-nuclear protests were reiterated in 1939 and 1951.

Split Poland on an ethno-Linguistic line?
The Venezuelan suggested in 1945 that Poland could be split on an ethno-Linguistic line. Hungary and Czechoslovakia had go neutral. Was also Germany to back off from Czech Prague, but keeps the German speaking Sudetenland as a gesture of good will.
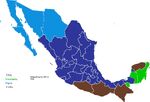
Venezuela's peace idea.
In 1946, Venezuela suggested split Mexico temporally and hold elections and reunite it as an independent state in 1947 or 1948.
Venezuela invited the Pontiff to Caracas, Maturín and Angle falls to help spread the Catholic faith further and inspire the rural poor with his Papal visit in or shortly after 1946, but he never came.
1947-1951[]
1947 saw Venezuela's government not file a patent for it's new ammonia fertilizers, so any one can use it freely in any nation with out copyrights, patents or costs other than (of course) paying their own people to make it. Farming out put increased by 5%- 6% for those who used it.
Venezuela proposed during 1948, the building a new railway linking the Mexican cities of Cancun, Tuxtla Gutiérrez via San Francisco de Campeche, Mexico City, Guatemala City, Acapulco, El Paso (Texas), Tecoman, Juarez, Mazatalan, and Villahermosa (Tabasco) in one united network rail network that the locals can enjoy and flourish under. Both Cuba, Japan, The UK, Germany, Italy, China, Hindustan and the USA are invited to set a join board for the joint run line. Venezuela suggested it so they have a veto and the fledgling Mayan Republic is on the board.
Venezuela recognised the new Spanish Republic that year. When China, Japan and Hindustan threatened to leave the UN Venezuela said it would not be leaving it, but that it would like an Hispanic nation on the permanent council.
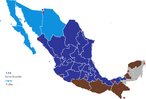
The Mexican cities linked by the proposed 1948 joint railway system.
Venezuela recognised the new Spanish Republic in early 1949. Venezuela’s ambassador to the UN had also raised concerns that the Security Council was to anti-Hispanic, because none of the 4 permanent members were of Hispanic origin by late 1949. this was all part of the Bolivarian plan to help rectify the injustices history had made towards the Hispanic cause.
Nicaraguan Canal which was a joint Chinese and Venezuelan ownership in the ratio 33%:66% (1:2) starts in 1949. China takes the majority of the cost of the project. It would be completed by mid-1956.
In 1950, Venezuela a 200 strong peace keeping force Colombia’s La Guajira Department due to the La Violencia (Spanish for- The Violence), a period of civil conflict in the Colombian countryside between supporters of the Colombian Liberal Party and the Colombian Conservative Party, a conflict which took place roughly from 1948 to 1958 (sources vary on the exact dates). The Venezuelan troops long stationed in the lawless Darién Gap as a security measure against a long passed Japanese invasion of Panamá then annex it to Venezuela. Latin American Economic and Monetary Union was founded later that year. VOIA agents, along with some local rebels, ambushed both Heinrich Himmler and Martin Bormann in their car to the south of Berlin, killing Bormann. Later special ops teams liberated the villages Balatonberény and Balatonszentgyörgy, next to Lake Balaton, from Nazi rule during 1950. The President flew to the Vatican to seek an audience with the Pope in the Holy See later that year. This year also saw a new oil fueled power station and several public air raid shelters are constructed in Caracas during 1950 and 1951.
Venezuela had gone to the UN in an attempt to end the UK's illegal occupation of Guayana Esequiba peacefully in 1950, but then went on to annex it along with the south of Trinidad island in early 1951.
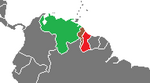
Guayana Esequiba is the Brown bit in Guayana.
A new natural gas fired power station opens in Cuaid de Guyana. Venezuela pulled out of the southern section south Trinidad as an act of good will to the UK. Commercial Peronin flights by Argentina are started to Venezuela.
The Hungarian lands of Kis-Balaton, Keszthely and Fonyod in Hungary were freed later in to in 1951. A joint Venezuelan-Ruthenian strike then freed German held Bohemia by the middle of the year and the Neo-Bolivarian Union came in to existence towards the end of 1951, all be it with a few days of illegal occupation by the USSR in the November of that year.
1952-1955[]
Venezuela started sponsoring and in some cases openly helped separatists in Cape Verde, Portuguese Guinea, Cabinda and São Tomé and Príncipe in from 1952 to 1954, as part of the fight against the then racist Portuguese government.

The flag of the 1952-57 Greek Colonels' regime.
The nation then tried to install Greek Colonel Ionnas Partrias Stakixs as dictator of the Greek mainland in 1952, but was forced to back down due to Soviet pressure, until 1954.
The Mexican railway project began that year in the Cuban and Mayan Republic’s sectors of Mexico. Full race and gender equality was introduced in Greater Venezuela.
As a result of the La Violencia getting noticeably worse, Venezuela invaded Colombia and started to root out the drug lords and leftist social detritus (the people who would create the OTL FARC movement) in the 1952-54 Narco-war with Colombia.
Venezuela thought stability could be brought to the remnant of Saudi Arabia through strong leadership. This was done via the Saudi Arabian revolt of 1953. The rebel sheiks in Anglo-Arabia were stopped later that year, removed and join Venezuelan Arabia's population.

Flag of Dhahran city state.

Madinah Caliphate's flag.
Cali fell to Venezuela forces, who had also pushed in to Colombia's Amazonas region. equal employment, legal and voting rights were given to all of Venezuela's citizens. Hindustan, Ethiopia and Sudan are offered an alliance. South Triada was evacuated of Venezuelan forces, wile Tobago and Guyana are peacefully assimilated in to Venezuela.
Free Bohemia was given full independence under the rule of the Christian democrat leader Igor Klauze. Venezuela denounced the illegal state of Vietnam by the middle of the year and called the Viet Minh rebels "lawless hooligans".
Urban student riots hit- El Distrito Metropolitano de Caracas (Metropolitan District of Caracas) and hooligans riot in the Distrito Capital (the capital city proper) and in the Chacao, Baruta, Sucre, and El Hatillo municipalities in Miranda State. The General Umberto Aznar University of engineering was opened that day, but nearly burnt down by angry teenagers and trades unionists. The riots were slowly fought back with teargas, water cannons and rubber-bullets.
Hindustan's friendly offer to help crush the Colombian rebels got out of hand and was abruptly canceled after they tried to attack friendly Peru in 1954, which then joined Venezuela's block (It had been planning to for the last five or so years any way).
In the August of that year VOIA agents hijacked the planned Paraguayan coup of 1954 and replace the OTL General Strossnder with the ATL Venezuelan yes-man Sergeant Juan Luigi Lorennzo.
Like-minded Bolivia got the political hints and joined the Bolivarian Union in mid 1954.
Ba'athist/Nasserite General Mohamed Yasser Hussein of Dammam city state is appointed PM of Venezuelan held Central Arabia and the minor royal Sheikh Abdu Ali bin-Falika bin Saud of Riyadh is declaimed king Emir until elections can be arranged.
Venezuela sends peace keepers to Harper, Liberia. The British Pitcairn Island (near Tahiti) is annexed as the 64 locals surrender to a Venezuelan fishing boat with a 0.50 machine gun, two rifles and a pistol on board it.
Due to obvious Geo-political circumstances, President Sadeq Ali Reza Abdul Rahimi of the long unrecognised state of Free Kurdistan joins forces with Venezuela rather than Hindustan or the British, or the USSR. Promises of Turkish territory and a protectorate were used to curry favor with the Kurds. Kurdistan expands westward toward the end of the year. A direct transit route from Persia to Turkey is created. Later Turkey's West coast would do likewise and form the state of Ismir after Venezuelan peace keeper ended a bitter six month war with Hindustan. The Soviet Union campaigned and invaded Kurdistan a few weeks later in a show of strength against Venezuela.
1954 saw the collapse of the N.U.M.A. and the capture of Norway's Antarctic territories, with various missions claiming neglected sub-Arctic islands during 1955. Both Bouvet Island and Lars Island were laid claim to in mid 1955. Colombia’s new borders were fully defined at the same time.
2,000 Venezuelan troopers, a M.A.C. ship, two MiG 15s copies and two Pena de muerte concepción class bombers went to the the lawless state of Liberia in 1955 after the Yugoslavs' delegation and the government negotiation team were attacked by local bandits. The campaign (with Spanish and Yugoslav help would last until 1957.
Post 1956[]
The Neo-Bolivar Union formally became a single federal republic based on the federal rules and ideas of the OTL USA.
The nationally renowned ATL Caracas Times, now Caracas TV journalist Mendoza Alfonse Sánchez (he’s somewhat between the OTL explorer Bare Grylls and OTL journalist Sir Richard Dimbelby) is sent on the most daring mission of his entire 22 years of reporting in mid 1957.
TV was tried out in La Plaz, Cali and Asunción. The OTL late 1950’s pilot system in Chile is expanded throughout the major urban centres of Chile.
Economics[]
Business sectors[]
| Sector. | % of national economy |
| Agriculture, floristry and fisheries | 25% |
| Mining and oil production/refining | 22% |
| Other primary services. | 10%. |
| Manufacturing services. | 31% |
| Tertiary services. | 5% |
| Tourism | 1% |
| Financial services | 1% |
| State service like policing | 5% |
Mineral resources[]
Oil (started in 1910), coal (started in 1900), natural gas (started in 1930), oil shale, sand, bauxite, iron ore, low grade gold and natural bitumen.
Natural resources[]
Timber, fruit and coffee.
Manufactured goods[]
T.V. sets, radios, packaging, processed food, cardboard, corrugated iron, ash-felt, bricks, cement, clothes, cloth, furniture and hand tools.
Demographics[]
General info.[]
About 85% of the population of Venezuela proper live in the growing urban areas in northern Venezuela and about 73% live less than 100 km (62 mi) from the coastline.
Infrastructure.[]
The federal telecommunications network, water supply, sewerage works and power grids are substantially improved across the union in 1957.
literacy[]
A national literacy campaign was launched in 1935. Several new schools open in the urban slums in 1945. A rural literacy campaign was begun and several new schools also open in the rural provinces during 1946. Male Literacy rates are 55% and Female literacy rates are 33% by 1949.
Universities[]
The General Umberto Aznar University of engineering was opened in 1953.
Ethnic groups[]
| Ethnic group. | % of population. |
| Mestizo | 48.5% |
| Spanish | 20% |
| Quechua | 7.5% |
| Aymará | 7% |
| Other Whites | 4.5% |
| Guarani | 4% |
| Germans | 1.1% |
| Chiolle, | 0.5% |
| Moche | 0.25% |
| British | 0.25% |
| Gyanan Negros | 0.25% |
| Kuna | 0.1% |
| Chibcha, | 0.1% |
| Carib | 0.1% |
| Arawak | 0.1% |
| Paez | 0.1% |
| Wayuu | 0.1% |
| Afro-Venezuelans | 0.25% |
| Yanomamis | 0.1% |
| Colombian Mulatos | 2% |
| Panamanian Mulatos | 0.25% |
| Yekuana | 0.1% |
| Other Amerindians | 0.25% |
| Chinese | 0.25% |
| Sumo | 0.1% |
| Palestinians | 0.1% |
The environment[]
(being heavily updated)
Venezuela lies within the Neotropic ecozone; large portions of the country were originally covered by moist broadleaf forests. One of seventeen mega-diverse countries and among the top twenty countries in terms of endemism, some 38% of the over 21,000 plant species are unique to the country; 23% of reptilian and 50% of amphibian species are also endemic.
Biodiversity[]
Venezuela hosts significant biodiversity across habitats ranging from xeric scrublands in the extreme northwest to coastal mangrove forests in the northeast. Its cloud forests and lowland rainforests are particularly rich, for example hosting over 25,000 species of orchids. These include the flor de mayo orchid (Cattleya mossiae), the national flower.
Nature reserves[]
A Venezuelan nature reserve is opened in the Sierra Pacaraima mountains on the border with Brazil in 1949 and the southernmost 33% of Amazonas province in 1950.
Green issues[]
Mercury levels are getting too high in the Orinoco and rubbish is a major problem in Caracas.
Media[]
Newspapers[]
Both censored state-run and privately run semi-censored newspapers have existed since the 1880’s.
Radio[]
Both censored state-run and privately run semi-censored radio stations have existed since the late 1920’s.
Cinemas[]
Four major drive-in cinemas were opened in the late 1940's. Two were in Caracas, one was in Ciudad Bolívar, with another in Ciudad de Guyana. A new one was opened in Panama city during 1956.
TV[]
Experimental TV broadcasts now start in Valladolid and Caracas during 1954, and then Ciudad Bolivar, Managua, Panama City and Bogotá in 1955. Broadcasts began in Lima during 1956. TV was tried out in La Plaz, Cali and Asunción in 1958. The OTL late 1950’s pilot system in Chile is expanded throughout the major urban centres of Chile.
Famous journalists[]
The nationally renowned ATL Caracas Times, now Caracas TV journalist Mendoza Alfonse Sánchez (he’s somewhat between the OTL explorer Bare Grylls and OTL journalist Sir Richard Dimbelby) is sent on the most daring mission of his entire 32 years of reporting in mid 1957. He went to Denmark, Estonia, Pomerania and southern Sweden to investigate suspected war crimes allegations. It was one of those 3 month undercover jobs like OTL journalists do in today’s N. Korea, Zimbabwe and Saddam’s Iraq. Mendoza’s report for Caracas TV can be found here Caracas TV war crimes report, March 2, 1958 (Axis vs. Allies). He worked between 1930 and 1962.
Military[]
The country has an air force, army, navy, missile command, customs service, coastal defence, river patrol and the V.O.I.A. secret service. For the individual service's statistics, see The military of the Venezuelan Republic (Axis vs. Allies)
Order of Battel[]
- 19 Infantry Divisions
- 3 Artillery regiments
- 1 Paratrooper Regiment
- 2 Mechanised Regiments
- 4 Armoured Companies
- 2 Transportation Regiments
- 2 Communications Companies
- 3 Engineering Companies
- 5 Fighter Wings
- 3 Bomber Wings
- 1 Strategic Wing
- 1 Multi-Purpose Wing
- Missile command
- The V.O.I.A. secret service
- Customs service
- Coastal defence
- Anti-aircraft defence
The Antarctic survey[]
The Venezuelan Antarctic Survey Board (V.A.S.B.) was set up in 1954 using an ex-Yugoslav Arctic Ice survey ship. It the charted and laid claim to Venezuela's slice of Antarctica from 1955 to 1956. The ship carries supplies to Venezuela's Antarctic bases on a regular basis. They also possess two Sikorsky H-5 equivalent helicopters.
Transport[]
Air mail[]
Venezuela opened its national air mail service in 1950, with three Stinson Reliant aircraft. Two Sikorsky H-5 equivalent helicopters were then added to its list in 1953, for work in the most remote parts of the Amazonas region.
Airlines[]
Two ‘Rodriguez type’ airliners, which is a copy of Poland's PWS-21 have done state sponsored flights to the neighbouring states since the early 1940's, but many entrepreneurs have set up local services with a few small passenger, freight and/or mail aircraft since 1930. A Martin M-130 air liner joined the state fleet in 1950, 1951 and 1952.
A Rodriguez type passenger plane started regular flight from Caracas to Buenos Aires via Ciudad de Guyana, Ciudad Bolivar, Rio De Janeiro and Montevideo in mid-1951. With this, the state owned airline “Aero Venezuela” is thus born.
Two Dehavilan Comet comparable aircraft would join the "Aero Venezuela" fleet in 1952 and would run regular flights to and from Panama City via Aruba. These were joined in 1953 by two Boeing 377 comparable civil airliners flying from Ciudad de Guyana to Panama City via Caracas, Aruba and Bogotá. Aero Venezuela then went on to use the Boeing 377 equivalent airliner to set up an air route from Caracas to Lima Via Quito later that year. They would also gain two LWD Junak equivalent trainer aircraft for their own corporate use rather than rely on the armed forces for future pilot training. "Aero Venezuela" used another two Boeing 377 equivalent airliners, in 1955, to set up an air route from Caracas to Santiago in Chile, via Lima via Quito.
Motorways[]
to be done
Railways[]
to be done
Venezuelan space travel program[]
A modified PGM-17 Thor missile copy was set up north of Ciudad Bolivar, and with this the Venezuela Space Agency (V.S.A.) was born in 1955. Venezuela joined the international EASA later in 1955 and two more Thor missile copies were added in 1956. The Venezuela Space Agency (V.S.A.) launched its first Thor missile copy from its facility in Ciudad Bolivar to see if its new and upgraded 'space tonic' fuel works. It did, and the missile safely splashed down of the coast of northern Peru on January 2nd, 1957.
Inventory of spacecraft-
- 2 Yugoslav Heinkel Tr 01s
- 3 modified PGM-17 Thor missile copy
Coast guard[]
The civil coast guard was created in 1952. Two Dornier Do 24 comparable air-sea rescue flying boats and three Sikorsky H-5 helicopter work for the national coast guard service.
Politics[]
The national policy is of a right-wing, pro-Latin and nationalistic type. The only election so far were in. 1939 elections fixed so General Umberto Aznar won with a majority of 99% over 1% on a turnout of 106% (~6% of the votes were forged).
List of Presidents of Venezuela[]
See- List of heads of state.

General Umberto Aznar.
- (OTL) Juan Vicente Gómez- 1908-1933.
- General Umberto Aznar- 1933-1951.
- Lieutenant General Oscar Aznar- 1951
- Air Commodore Rodríguez Gilberto Miguel Orejuela- 1951
- Lieutenant General Oscar Aznar- 1951-1958.
- Air Commodore Rodríguez Gilberto Miguel Orejuela- 1958
- Col. Juan Vincent Aznar- 1958-1964
- Diego Philliepe Aznar (14 year old son of Oscar, hire apparent after age 21)
Famous women[]

Lt. Gen. Oscar Aznar's Yekuana Indian wife Maria.
Lt. Gen. Oscar Aznar's sweet Yekuana Indian wife Maria, who was not born with a second name, since her clan had yet to understand what family names were.

Col. Juan Vincent Aznar's Hindustani wife Priyanka Hiduerna.
Col. Juan Vincent Aznar married a wealthy Hidustani ex-pat named Priyanka Hiduerna.]]
Diplomacy[]
The Latin American Economic and Monetary Union (LAEMU) was founded in mid 1951 by the states of Venezuela, Ecuador, Colombia, Trinidad and Tobago, Bolivia, Paraguay, Peru and Chile.
The Venezuelan government then set up the League of Catholic Nations later in the year as a mutual religious, cultural, trade and defence pact. The founding members were Venezuela, Colombia, Italy and Argentina. Brazil joined in 1952.
The Neo-Bolivarian Union was created out of Panama, El Salvador, eastern Nicaragua, Venezuela and Guyana Esequiba merging into a united federation of autonomous states (like the OTL USA and its states) in in 1951, which came into force on January 1 1953.
The nations of the Neo-Bolivarian Union form a OTL USA style federation. They consist of Venezuela, and its satellite states of Guyana, Tobago, Panama, Nicaragua, the Netherlands Antilles, El Salvador, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia and Paraguay.
The U.N.[]
Venezuela put forward these security council resolutions-
- UN Resolution #6: Regarding the ownership of the Falkland Islands, Shag Rocks, Black Rocks and South Georgia.
- UN Resolution #7: Helping Scandinavia after the 1952-55 nuclear war.
Client states and dependencies[]
The Mayan Republic (client)[]

The Mayan Republic flag
Population (1951)- 1,720,000.
Location- S. W. Mexico.
Capital- Cancun.
Ruthenia-Nyíregyháza (client)[]
Capital-Kust.
Trebisov and Košice (merged with Ruthenia)[]

Trebisov and Košice flag
Population (1958)- Trebisov- 42,000 and Košice 135,000.
Location- S.E. Slovakia.
Capital- Košice
Nyíregyháza (merged with Ruthenia)[]

flag of Nyíregyháza.
Population (1958)- 46,500 in Nyíregyháza and 49,550 in Nyíregyháza district, et al.
Location- eastern Hungary.
Capital- Nyíregyháza
Ruthenia (client)[]

The flag of Ruthenia.
Poulation (1958)- 805,000.
Location- Ruthenia.
Capital- Kust
Mt Tarnica, et al (merged with Poland)[]

The flag of Mount Tarnica.
Population (1962)- 47 (Mt. Tarnica), Tarnica Village 138
Location- S.E. Poland [1].
Capital- The Shepard’s hamlet on Mt Tarnica.
Oberlichtenau-Niederlichtenau-Pulsnitz (now an Austrian client)[]

The flag of the villages of Oberlichtenau-Niederlichtenau.
Population (1958)-1990 Oberlichtenau-Niederlichtenau & 4550 Pulsnitz
Location- Eastern Germany.
Capital- Oberlichtenau.
The free state of Lake Balaton (Semi-client, Independence ~1954?)[]
Capital- Balatonberény
Balatonszentgyörgy-Balatonberény (merged in to The free state of Keszthely)[]

The flag of Balatonszentgyörgy-Balatonberény state
Population (1950)-1,500 Balatonszentgyörgy-Balatonberény and 3,000 Hévíz
Location- western Hungary.
Capital- Balatonberény
The Free state of Keszthely, Fonyód and the Kis-Balaton wetlands (Semi-client)[]

The Fonyód and Keszthely free state flag.
Population (1950)- 16,100.
Location- western Hungary.
Capital- Balatonberény
Free Bohemian republic[]

The Free Bohemian Flag.
Population (1950)- 3,550,000.
Location- Bohemia.
Capital- Prague
Free Guiné (now a de facto Portuguese client)[]

The flag of Free Guiné.
Population (1955 est.)- 775,000
Location- West Africa.
Capital- Bissau.
Sao Tome, Principe and Cabinda (dependency)[]

The Sao Tome, Principe and Cabinda flag
Population (1955 est)- 778,000
Location- Central Africa.
Capital- Cabinda.
Bouvet and Lars Island, et al's flag (dependency)[]

Bouvet and Lars Island, et al's flag.
Population (1955 est,)- 42 Norwegian scientists, 12 Venezuelans and 10,000 penguins.
Location- Antarctica.
Capital- Bouvet island's Norwegian weather station.
South Orkneys, Hope bay, et al's flag (dependency)[]

South Orkneys, Hope bay, et al's flag (dependency)
Population (1955 est.,)- 32 Venezuelans, two Peruvians and 25,000 penguins.
Location- Antarctica.
Capital- Hope Bay's Venezuelan scientific station
Democratic Ismir (protectorate)[]

The flag of Ismir.
Population (1964 est.,)- 7,000,300.
Location- Western Turkey
Capital- Ismir until 1957, Istanbul thereafter.
Sudan (emergency rule, now independent)[]

The Sudanese flag.
Population (1960 est.,)- 4,750,000.
Location- North Africa.
Capital- Khartoum.
Fascist Greece (protectorate)[]

The flag of the 1952-57 Greek Colonels' regime.
Population (1964 est.,)- 4,460,000.
Location- Greece.
Capital- Athens.
Sports[]
The national football and Rugby teams were formed in late Victorian times and Venezuela went on to set up a Formula 1 (F-1 racing) team in 1950. A cricket team was founded in 1951.
Also see[]
- Axis vs Allies Revised national flags
- Caracas TV war crimes report, March 2, 1958 (Axis vs. Allies)











