Mexico Timeline: Zimmermann | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: Tierra y Libertad "Land and Freedom" |
||||||
| Anthem: Himno Nacional Mexicano |
||||||
| Location of Mexico in North America
|
||||||
| Capital | Mexico City | |||||
| Largest city | Mexico City, Disctrict of Anahuác | |||||
| Official languages | Spanish | |||||
| Government | Federal presidential constitutional republic | |||||
| - | President | Ifigenia Martínez | ||||
| Legislature | Supreme Congress of Mexico | |||||
| - | Upper house | Senate of the federation | ||||
| - | Lower house | Chamber of Deputies | ||||
| Establishment | ||||||
| - | Independence from Spain | 16 September 1810 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 2,374,611 km2 916,842 sq mi |
||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | Estimate | 132,750,300 (2017) (8th) | ||||
| Currency | Peso | |||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
Alternative History: Imagine if the Zimmermann Telegram had not been intercepted and cracked by Britain in 1917 and Mexico had joined the war against the Entente. The lack of American troops on the Western Front would have very little impact on the course of the war but, what about the Second World War? How would it be affected? This time line also has several other POD's which will be mentioned later.
Mexico, officially the Federal Mexican Republic, is a federal republic in the southernmost portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the south east by Central America, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. With an estimated population of over 130 million people, the country is the most populous Spanish-speaking state in the world, the second-most populous country in North America, and the eighth-most populous nation in the world. Mexico is a federation comprising 31 states and Mexico City, a special federal entity that is also the capital city and its most populous city. Other metropolises in the state include Guadalajara, Monterrey, Puebla, Toluca.
History (Alternative)[]
Zimmermann Telegram[]
The Zimmermann Telegram was a 1917 diplomatic proposal from the German Empire to Mexico to make war against the United States. The proposal was accepted by Mexico who later went on to invade the United States after she declared war in the May of 1917.
Sinking of the Mauretania[]
The passenger liner Mauretania (there were no Gallipoli landings in this time line) was sunk by German submarine U-20 (the same submarine which had sunk the Lusitania) on April 30th 1917, roughly 300 miles west of Ireland. There were 296 American passengers on board, all of whom perished in the sinking. The sinking eventually caused the U.S congress to declare war on Germany and her allies (excluding Mexico).
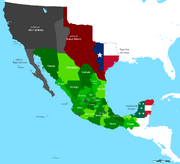
Mexico territory in 1841.
Entry of Mexico[]
The United States began sending many thousands of U.S soldiers to Europe (much faster than in OTL) and by July 1917 over 15,000 American soldiers were in or on their way to the trenches. On August 1st Mexico launched an invasion of the U.S states of California, Texas and New Mexico.
Initial Mexican Invasion[]
Initial resistance to the Mexican invasion in New Mexico and California was light and by October, Las Vegas was under siege, San Diego and San Bernardino had fallen and a Battle was raging across Los Angeles. In Texas, however, resistance was much heavier, in comparison, although El Paso had fallen, Mexican troops had sustained heavy casualties.
Politics[]

Mexican Federation flag.

Coat of arms.
Government[]
The Federal Republic of Mexico is a federation whose government is representative, democratic and republican based on a semipresidential system according to the 1917 Constitution. The constitution establishes three levels of government: the federal Union, the state governments and the municipal governments. According to the constitution, all constituent states of the federation must have a republican form of government composed of three branches: the executive, represented by a governor and an appointed cabinet, the legislative branch constituted by a unicameral congress and the judiciary, which will include a state Supreme Court of Justice. They also have their own civil and judicial codes.
The federal legislature is the bicameral Congress of the Union, composed of the Senate of the Republic and the Chamber of Deputies. The Congress makes federal law, declares war, imposes taxes, approves the national budget and international treaties, and ratifies diplomatic appointments.
The federal Congress, as well as the state legislatures, are elected by a system of parallel voting that includes plurality and proportional representation. The Chamber of Deputies has 500 deputies. Of these, 300 are elected by plurality vote in single-member districts (the federal electoral districts) and 200 are elected by proportional representation with closed party lists for which the country is divided into five electoral constituencies. The Senate is made up of 128 senators. Of these, 64 senators (two for each state and two for Mexico City) are elected by plurality vote in pairs; 32 senators are the first minority or first-runner up (one for each state and one for Mexico City), and 32 are elected by proportional representation from national closed party lists.
The executive is the President of the United Mexican States, who is the head of state and government, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Mexican military forces. The President also appoints the Cabinet and other officers. The President is responsible for executing and enforcing the law, and has the power to veto bills.
The highest organ of the judicial branch of government is the Supreme Court of Justice, the national supreme court, which has eleven judges appointed by the President and approved by the Senate. The Supreme Court of Justice interprets laws and judges cases of federal competency. Other institutions of the judiciary are the Federal Electoral Tribunal, collegiate, unitary and district tribunals, and the Council of the Federal Judiciary.
| |||||
| Capital | Mexico City | ||||
| Largest city | Mexico City | ||||
| Other cities | Veracruz, Tampico | ||||
| Language | Spanish | ||||
| Religion | Atheism, Catholicism | ||||
| Government | Socialist (Trotskyism) | ||||
| Premier | |||||
| Secretary of the Politburo | |||||
| Currency | Peso | ||||
Politics[]
Three parties have historically been the dominant parties in Mexican politics: the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI), a catch-all party and member of the Socialist International that was founded in 1929 to unite all the factions of the Mexican Revolution and held an almost hegemonic power in Mexican politics since then; the National Action Party (PAN), a conservative party founded in 1939 and belonging to the Christian Democrat Organization of America; and the Party of the Democratic Revolution (PRD) a left-wing party, founded in 1989 as the successor of the coalition of socialists and liberal parties. PRD emerged after what has now been proven was a stolen election in 1988, and has won numerous state and local elections since then. PAN won its first governorship in 1989, and won the presidency in 2000 and 2006.
A new political party, National Regeneration Movement (MORENA), a leftist-populist party, emerged after the 2012 election and dominated the 2018 Mexican general election.
Unlike many Latin American countries, the military in Mexico does not participate in politics and is under civilian control.
Administrative divisions[]

Map of 50 mexico departments.
The Mexican Federation have 50 departments, which form a union that exercises a degree of jurisdiction over Mexico City.
Each department has its own congress, and a judiciary, and its citizens elect by direct voting a governor for a six-year term, and representatives to their respective unicameral state congresses for three-year terms.
Mexico City is a special political division that belongs to the federation as a whole and not to a particular state. Formerly known as the Federal District, its autonomy was previously limited relative to that of the states. It dropped this designation in 2016 and is in the process of achieving greater political autonomy by becoming a federal entity with its own constitution and congress.
The states are divided into municipalities, the smallest administrative political entity in the country, governed by a mayor or municipal president (presidente municipal), elected by its residents by plurality.





